| Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| Targets |
COX
|
|---|---|
| ln Vivo |
To evaluate the effects of aspirin on thrombin generation in patients with unstable angina, plasma levels of thrombin-antithrombin III complex (TAT) as a new marker of thrombin generation and of 11-dehydro-thromboxane B2 (11-dehydro-TXB2) as an indicator of platelet activation were measured in 18 patients with unstable angina, including 8 patients with prolonged rest angina (> 15 minutes). Aspirin DL-lysine (900 mg) was administered intravenously to 9 of the 18 patients (aspirin group); the other 9 were not given aspirin during the first 24 hours of hospitalization (non-aspirin group). Clinical characteristics, angiographic features and medications other than aspirin were similar between the 2 groups. Levels of plasma TAT and 11-dehydro-TXB2 were significantly higher (p < 0.05) in patients with prolonged rest angina than in those without the condition (n = 10). In 5 patients with prolonged rest angina who received aspirin, plasma TAT levels (ng/ml) were significantly decreased (4.52 +/- 1.18 at baseline, 2.50 +/- 0.65 at 1 hour and 2.16 +/- 0.42 at 24 hours after aspirin administration, p < 0.01) with a significant decrease in plasma 11-dehydro-TXB2 levels. However, the reduction in TAT after aspirin administration was slight in patients without prolonged rest angina (n = 4). In contrast, levels of plasma TAT and 11-dehydro-TXB2 in the non-aspirin group remained unchanged during the study period. These results suggest that aspirin rapidly reduces thrombin generation through inhibition of platelet activity in patients with unstable angina with prolonged rest angina[1].
|
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Aspirin DL-Lysine is the lysine salt form of acetylsalicylic acid, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activities. Like other NSAIDs, aspirin DL-lysine inhibits the activity of cyclooxygenase I and II, resulting in decreased formation of prostaglandins (PGs) and thromboxanes precursors. This leads to decreased PG synthesis by PG synthase. This agent also causes a decrease in the formation of thromboxane A2 synthesis by thromboxane synthase, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation.
|
| Molecular Weight |
326.34498
|
|---|---|
| Exact Mass |
326.147
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 55.21; H, 6.80; N, 8.58; O, 29.41
|
| CAS # |
62952-06-1
|
| Related CAS # |
Aspirin;50-78-2; 50-78-2; 69-46-5 (calcium); 62952-06-1 (lysine); 23413-80-1 (Aspirin Aluminum); 552-98-7 (lithium); Deuterated Aspirin 921943-73-9; 97781-16-3
|
| PubChem CID |
9905405
|
| Appearance |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| Density |
321.4ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| Boiling Point |
321.4ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| Melting Point |
154-156ºC
|
| Flash Point |
131.2ºC
|
| LogP |
2.238
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
4
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
8
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
8
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
23
|
| Complexity |
318
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
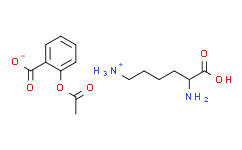
[NH3+]CCCCC(C(=O)O)N.CC(OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
JJBCTCGUOQYZHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H8O4.C6H14N2O2/c1-6(10)13-8-5-3-2-4-7(8)9(11)12;7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(9)10/h2-5H,1H3,(H,11,12);5H,1-4,7-8H2,(H,9,10)
|
| Chemical Name |
2-acetyloxybenzoic acid;2,6-diaminohexanoic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Aspirin DL-lysine; DL-Lysine acetylsalicylate; 62952-06-1; Egicalm; Aspirisine; Aspegic; Aspidol; Solpirin; ASL; DL-Lysine acetylsalicylic acid salt; Aspisol;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples.
Injection Formulations
Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] Oral Formulations
Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0642 mL | 15.3210 mL | 30.6419 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6128 mL | 3.0642 mL | 6.1284 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3064 mL | 1.5321 mL | 3.0642 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.