
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
Purity: ≥98%
AZD4547 (AZD-4547; AZD 4547) is a novel and orally bioavailable FGFR (fibroblast growth factor receptor) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. In cell-free assays, it inhibits FGFR1/2/3 with IC50s of 0.2 nM/2.5 nM/1.8 nM. However, its activity against other kinases, including FGFR4, VEGFR2(KDR), IGFR, CDK2, and p38, is minimal or weaker. Significant tumor-suppressive effects of AZD4547 are observed in mice with KMS11 tumors with a TGI of 53%.
| Targets |
FGFR1 (IC50 = 0.2 nM); FGFR2 (IC50 = 2.5 nM); FGFR3 (IC50 = 1.8 nM); FGFR4 (IC50 = 165 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Fexagratinib also inhibits recombinant VEGFR2 (KDR) kinase activity with an IC50 of 24 nM. Fexagratinib exhibits a powerful inhibition of autophosphorylation of FGFR1, 2, and 3 tyrosine kinases (IC50 values of 12, 2, and 40 nM, respectively) in KG1a, Sum52-PE, MCF7, and KMS11 cell lines. However, it lessens the inhibition of FGFR4 cellular kinase activity (IC50=142 nM). Compared to cellular KDR and IGFR ligand-induced phosphorylation, significantly lower inhibitory activity is seen (IC50 values of 258 and 828 nM, respectively), indicating selectivity over cellular FGFR1 of about 20 and 70 times, respectively. Furthermore, FGFR phosphorylation and downstream signaling mediated by FRS2, PLCγ, and MAPK are potently inhibited by fexagratinib at the cellular level[1].
|
| ln Vivo |
Fexagratinib is administered chronically at various well-tolerated doses to female SCID mice with KMS11 tumors. The mice are treated in a randomized manner. Tumor growth inhibition is dose-dependent when administered orally with Fexagratinib. When compared to vehicle-treated controls, the administration of Fexagratinib at a dose of 3 mg/kg twice a day results in a statistically significant tumor growth inhibition of 53% (P0.0005 by one-tailed t test), whereas doses of 12.5 mg/kg once daily and 6.25 mg/kg twice a day result in complete tumor stasis (P0.0001). Fexagratinib at a dose of 12.5 mg/kg once daily in the KG1a model was found to be 65% effective in inhibiting tumor growth (P=0.002)[1].
|
| Enzyme Assay |
AZD4547 is tested with ATP concentrations at or slightly below the corresponding Km to see if it can inhibit the human recombinant kinase activities of FGFR1-3).
In vitro protein expression analysis and kinase inhibition studies[1] Cells were treated with AZD4547 or control for 3 hours at 37°C and then stimulated with 10 ng/mL aFGF/bFGF and 10 μg/mL heparin for 20 minutes. Western blotting was conducted with standard SDS-PAGE procedures and antibody incubation carried out overnight at 4°C. Antibodies were obtained from the following sources: FGFR1, FGFR2 and FRS2, FGFR3 proteins, α-tubulin-B512 and Bcl2, and BIM. Secondary antibodies were applied and immunoreactive proteins visualized with “SuperSignal West Dura” Chemiluminescence substrate according to the manufacturer's instructions. Inhibition of cellular receptor phosphorylation[1] For FGFR phosphorylation studies, FGFR1, 3, or 4–transfected Cos-1 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 2 mmol/L l-glutamine and 3% FCS. For FGFR2, Sum52-PE cells were cultured in RPMI-1640, growth media supplemented with 2 mmol/L l-glutamine and 10% FBS. Following 1-hour incubation with AZD4547, media were removed; cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then incubated with monoclonal anti-phospho-FGFR antibody (Cell Signaling Technology; 1:1,000) for 1 hour followed by incubation with anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 594 secondary antibody (1:500) and Hoechst (1:1,000) for 1 hour. Fluorescence measurement was conducted with Arrayscan. For KDR phosphorylation studies, primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells were obtained from PromoCell and cultured according to the supplier's protocol. Cells were incubated with AZD4547 for 90 minutes and then stimulated for 5 minutes with VEGF ligand (25 ng per well). Cells were lysed with standard radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer containing phosphatase/protease inhibitors. Lysates were analyzed with the human phospho-VEGF R2 ELISA protocol according to the manufacturer's instructions. For insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) phosphorylation studies, R+ cells were derived from murine transgenic IGF1R knockouts and then stably transfected with human IGF1R. Cells cultured in DMEM supplemented with 1% heat-inactivated FCS and 1% l-glutamine were incubated with AZD4547 and then stimulated with IGF ligand, followed by fixation, blocking, and incubation with a rabbit anti-phospho IGF1R/IR antibody (1:350) for 1 hour. Secondary detection and measurement was carried out with an Acumen Explorer HTS Reader at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and emission wavelength of 530 nm. |
| Cell Assay |
For 72 hours, cell lines are incubated with AZD4547 at fixed concentrations. Cells are fixed with 70% ethanol and then incubated with a propidium iodide/RNase A labeling solution for fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). CellQuest analysis software and an FACSCalibur instrument are used to evaluate cell-cycle profiles. Cells and media are carefully collected, centrifuged, and cell pellets are then washed in preparation for apoptotic analysis. Following that, the cells are prepared for propidium iodide uptake and FITC staining. A FACSCalibur device is then used to determine the percentage of cells that stain positively for Annexin V, and CellQuest analysis software is used to sort the cells into quadrants[1].
|
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: The mice used are Swiss-derived nude (nu/nu) and severe combined immunodeficient (SCID). Tumor xenografts are created by injecting 0.1 mL (1×106 for LoVo, 1×107 for HCT-15, and 1×107 for Calu-6) or 0.2 mL (2×107 for KMS11 and KG1a) of tumor cells mixed 1:1 with Matrigel into the left flank, with the exception of LoVo and HCT-15, which do not include Matrigel. Tumors that are larger than 0.2 cm3 are randomly assigned to treatment and control groups, and mice are given AZD4547 (1.5-50 mg/kg) orally once or twice a day. For the duration of the study, tumor condition, animal body weight, and tumor volume (measured using a caliper) are recorded twice a week. One computes the tumor volume.
|
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
AZD4547 is a member of the class of benzamides that is a carboxamide resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-(cis-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoic acid with the amino substituent of 5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-amine. It is an inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR). It has a role as a fibroblast growth factor receptor antagonist. It is a member of pyrazoles, a N-arylpiperazine and a member of benzamides.
AZD4547 has been used in trials studying the treatment of Cancer, LYMPHOMA, Gastric Cancer, Adenocarcinoma, and Solid Neoplasm, among others. Fexagratinib is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) with potential antineoplastic activity. fexagratinib binds to and inhibits FGFR, which may result in the inhibition of FGFR-related signal transduction pathways, and, so, the inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and tumor cell death. FGFR, up-regulated in many tumor cell types, is a receptor tyrosine kinase essential to tumor cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. The fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling axis is increasingly implicated in tumorigenesis and chemoresistance. Several small-molecule FGF receptor (FGFR) kinase inhibitors are currently in clinical development; however, the predominant activity of the most advanced of these agents is against the kinase insert domain receptor (KDR), which compromises the FGFR selectivity. Here, we report the pharmacologic profile of AZD4547, a novel and selective inhibitor of the FGFR1, 2, and 3 tyrosine kinases. AZD4547 inhibited recombinant FGFR kinase activity in vitro and suppressed FGFR signaling and growth in tumor cell lines with deregulated FGFR expression. In a representative FGFR-driven human tumor xenograft model, oral administration of AZD4547 was well tolerated and resulted in potent dose-dependent antitumor activity, consistent with plasma exposure and pharmacodynamic modulation of tumor FGFR. Importantly, at efficacious doses, no evidence of anti-KDR-related effects were observed, confirming the in vivo FGFR selectivity of AZD4547. Taken together, our findings show that AZD4547 is a novel selective small-molecule inhibitor of FGFR with potent antitumor activity against FGFR-deregulated tumors in preclinical models. AZD4547 is under clinical investigation for the treatment of FGFR-dependent tumors.[1] |
| Molecular Formula |
C26H33N5O3
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
463.57
|
| Exact Mass |
463.258
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 67.36; H, 7.18; N, 15.11; O, 10.35
|
| CAS # |
1035270-39-3
|
| Related CAS # |
1035270-39-3;1394854-62-6;
|
| PubChem CID |
51039095
|
| Appearance |
white solid powder
|
| Density |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| Boiling Point |
621.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| Flash Point |
329.8±31.5 °C
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.602
|
| LogP |
3.46
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
6
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
8
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
34
|
| Complexity |
622
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
2
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])N1C([H])([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])N([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C1([H])[H])N([H])C1C([H])=C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C2C([H])=C(C([H])=C(C=2[H])OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])N([H])N=1
|
| InChi Key |
VRQMAABPASPXMW-HDICACEKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H33N5O3/c1-17-15-31(16-18(2)27-17)22-9-6-20(7-10-22)26(32)28-25-13-21(29-30-25)8-5-19-11-23(33-3)14-24(12-19)34-4/h6-7,9-14,17-18,27H,5,8,15-16H2,1-4H3,(H2,28,29,30,32)/t17-,18+
|
| Chemical Name |
N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3S,5R)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]benzamide
|
| Synonyms |
fexagratinib; AZD-4547; AZD 4547; fexagratinib; N-(5-(3,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-((3S,5R)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide; AZD 4547; 2167OG1EKJ; N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]benzamide; AZD4547
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.39 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 4% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O: 5mg/mL Solubility in Formulation 5: 3.33 mg/mL (7.18 mM) in 1% CMC-Na/saline water (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication (<60°C). Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1572 mL | 10.7859 mL | 21.5717 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4314 mL | 2.1572 mL | 4.3143 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2157 mL | 1.0786 mL | 2.1572 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02299999 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: AZD2014 Drug: AZD4547 |
Metastatic Breast Cancer | UNICANCER | April 7, 2014 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02664935 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: AZD4547 Drug: Vistusertib |
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Adenocarcinoma |
University of Birmingham | May 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02546661 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: AZD4547 Drug: MEDI4736 |
Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer | AstraZeneca | October 3, 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05775874 | Recruiting | Drug: AZD4547 Drug: Tislelizumab |
Urothelial Carcinoma | Abbisko Therapeutics Co, Ltd | September 30, 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05086666 | Recruiting | Drug: AZD4547 | Urothelial Carcinoma | Abbisko Therapeutics Co, Ltd | June 3, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
|
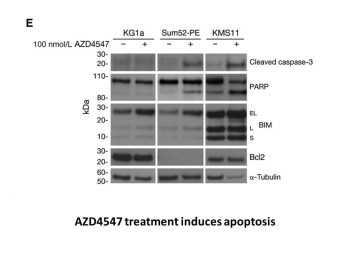 |
AZD4547 exposure correlates with in vivo antitumor activity, pharmacodynamic modulation of phospho-FGFR, and reduced tumor cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 15;72(8):2045-56. |