
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Everolimus (formerly also known as RAD001, SDZ-RAD, or the 40-O-(2-hydroxyethyl) derivative of sirolimus) is a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) with immunosuppressive activity. In a cell-free assay, it inhibits mTOR with an IC50 range of 1.6–2.4 nM. It forms an everolimus-FKBP12 complex by binding to the intracellular receptor FKBP12 in the mTOR pathway with high affinity. The complex also binds to mTOR, which inhibits the activity of downstream effectors S6 ribosomal protein kinase (S6K1) and eukaryotic elongation factor 4E-binding protein (4EBP), as well as mTOR itself. Everolimus is sold as a transplantation drug under the trade names Zortress (USA) and Certican (EU and other countries), and for oncological uses as Afinitor (general tumors) and Votubia (tumours resulting from TSC).
| Targets |
mTOR (IC50 = 5-6 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Everolimus (RAD001) is an orally active derivative of rapamycin that inhibits the Ser/Thr kinase, mTOR[1]. Antiproliferative concentrations of Everolimus cause total dephosphorylation of S6K1 and the substrate S6 in both the sensitive murine B16/BL6 melanoma (IC50, 0.7 nM) and the insensitive human cervical KB-31 (IC50, 1,778 nM) as well as a shift in the mobility of 4E-BP1, which is suggestive of a reduced phosphorylation status[3]. Although to varying degrees, everolimus inhibits the growth of both the total cells, the stem cells, and the primary breast cancer cells from the BT474 cell line. Everolimus is less effective at inhibiting stem cell growth at all tested concentrations when compared to the total number of cells (P<0.001). Everolimus has an IC50 for BT474 and primary CSCs of 2,054 and 3,227 nM, respectively, which is 29 and 21 times greater than the IC50 for the corresponding total cells[4].
|
| ln Vivo |
Everolimus is orally active in both mice and rats, producing an antitumor effect that is characterized by dramatic reduction in tumor growth rates as opposed to producing tumor regressions. Everolimus (0.5 or 2.5 mg/kg) daily treatment inhibits tumor growth in the rat CA20498 model in a dose-dependent manner, and intermittent administration of a higher dose of 5 mg/kg (once or twice per week) also exhibits comparable antitumor efficacy. Everolimus inhibition is not accompanied by any loss of body weight and is characterized by sustained suppression as opposed to regression[1]. Everolimus treatment (0.1–10 mg/kg/d) has a selective effect that is different from PTK/ZK treatment (100 mg/kg). Everolimus increases hemoglobin content, which is a measure of the number of vessels and their leakiness when converted to blood equivalents, when either growth factor is present. However, Everolimus decreases Tie-2 content, which is significant for VEGF stimulation but not bFGF stimulation. According to the pharmacokinetics of Everolimus in mice, plasma levels only reach 1 to 3 μM for about 4 hours while maximum levels of only 0.1 M are found in a human tumor xenograft after a single administration[3].
|
| Enzyme Assay |
FKBP12 binding assay: An ELISA-xstyle competition assay is used to inadvertently measure binding to the FK 506 binding protein (FKBP12). Each experiment uses FK 506 as a standard, and the inhibitory activity is expressed as a relative IC50 (rIC50 = IC50 Everolimus/IC50 FK 506) in comparison to FK 506. Using the spleen cells from BALB/c and CBA mice, the immunosuppressive effects of RAP and its derivatives are examined in a two-way mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR). Since RAP serves as a standard in each experiment, the inhibitory activity is expressed as a relative IC50 (rIC50 = IC50 Everolimus/IC50 RAP) in comparison to RAP.
|
| Cell Assay |
In 96-well plates, tumor cells are plated at densities ranging from 500 to 5,000/100 μL/well. Repeat experiments are then carried out with an optimal cell density, typically 1,000 to 2,000 cells per well, and incubated overnight. Methylene blue staining is used to count the cells after they have been exposed to Everolimus and incubated for 4 days. To do this, wells are filled with 50 μL of [20% (v/v)] glutaraldehyde and left to sit for 10 minutes at room temperature. Incubate 100 L of methylene blue [0.05% (w/v) in water] for 10 minutes at 37°C after aspirating the culture medium, washing the cells with distilled water, and adding the dye.
|
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: Everolimus, PTK/ZK, and their respective vehicles are prepared each day just before administration to animals and the administration volume is individually adjusted based on animal body weight. Everolimus is given to C57/BL6 mice at doses ranging from 0.1 to 10 mg/kg/d orally (10 mL/kg), with 2.5 to 10 mg/kg being the most frequently used dose because it has the greatest impact. PTK/ZK is given orally at a dose of 50 to 100 mg/kg/d.
Rats: Based on body weight, Wistar-Furth rats are divided into two equal groups and given either a control dose of the drug or Everolimus (10 mg/kg/d orally in mice and 5 mg/kg three times per week orally in rats). Everolimus or vehicle is given orally by gavage (10 mL/kg) for a maximum of 7 days, with subsequent magnetic resonance measurements taken within 30 minutes of the last dose. This is done immediately after the initial measurement at baseline (day 0). |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In patients with advanced solid tumors, peak everolimus concentrations are reached 1 to 2 hours after administration of oral doses ranging from 5 mg to 70 mg. Following single doses, Cmax is dose-proportional between 5 mg and 10 mg. At doses of 20 mg and higher, the increase in Cmax is less than dose-proportional, however AUC shows dose-proportionality over the 5 mg to 70 mg dose range. Steady-state was achieved within 2 weeks following once-daily dosing. Dose Proportionality in Patients with SEGA (subependymal giant-cell astrocytomas) and TSC (tuberous sclerosis complex): In patients with SEGA and TSC, everolimus Cmin was approximately dose-proportional within the dose range from 1.35 mg/m2 to 14.4 mg/m2. After a single dose of radiolabeled everolimus was given to transplant patients receiving cyclosporine, the majority (80%) of radioactivity was recovered from the feces and only a minor amount (5%) was excreted in urine. The blood-to-plasma ratio of everolimus is 17% to 73%. Following a 3 mg radiolabeled dose of everolimus, 80% of the radioactivity was recovered from the feces, while 5% was excreted in the urine. The blood-to-plasma ratio of everolimus is concentration dependent ranging from 17% to 73% over the range of 5 ng/mL to 5000 ng/mL. Plasma protein binding is approximately 74% in healthy subjects and in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. The apparent distribution volume associated with the terminal phase (Vz/F) from a single-dose pharmacokinetic study in maintenance kidney transplant patients is 342 to 107 L (range 128 to 589 L). The blood-to-plasma ratio of everolimus, which is concentration-dependent over the range of 5 to 5000 ng/mL, is 17% to 73%. The amount of everolimus confined to the plasma is approximately 20% at blood concentrations observed in cancer patients given Afinitor 10 mg/day. Plasma protein binding is approximately 74% both in healthy subjects and in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. After administration of Afinitor tablets in patients with advanced solid tumors, peak everolimus concentrations are reached 1 to 2 hours after administration of oral doses ranging from 5 mg to 70 mg. Following single doses, Cmax is dose-proportional with daily dosing between 5 mg and 10 mg. With single doses of 20 mg and higher, the increase in Cmax is less than dose-proportional, however AUC shows dose-proportionality over the 5 mg to 70 mg dose range. Steady-state was achieved within 2 weeks following once-daily dosing. No specific elimination studies have been undertaken in cancer patients. Following the administration of a 3 mg single dose of radiolabeled everolimus in patients who were receiving cyclosporine, 80% of the radioactivity was recovered from the feces, while 5% was excreted in the urine. The parent substance was not detected in urine or feces. The mean elimination half-life of everolimus is approximately 30 hours. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for EVEROLIMUS (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Everolimus is a substrate of CYP3A4 and PgP (phosphoglycolate phosphatase). Three monohydroxylated metabolites, two hydrolytic ring-opened products, and a phosphatidylcholine conjugate of everolimus were the 6 primary metabolites detected in human blood. In vitro, everolimus competitively inhibited the metabolism of CYP3A4 and was a mixed inhibitor of the CYP2D6 substrate dextromethorphan. Everolimus is a substrate of CYP3A4 and PgP. Following oral administration, everolimus is the main circulating component in human blood. Six main metabolites of everolimus have been detected in human blood, including three monohydroxylated metabolites, two hydrolytic ring-opened products, and a phosphatidylcholine conjugate of everolimus. These metabolites were also identified in animal species used in toxicity studies, and showed approximately 100-times less activity than everolimus itself. Everolimus has known human metabolites that include (1R,9S,12S,15R,16Z,18R,19R,21R,23S,24E,30S,32S,35R)-1,18-dihydroxy-12-[(2R)-1-[(1S,3R,4R)-3-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)cyclohexyl]propan-2-yl]-19,30-dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-hexamethyl-11,36-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[30.3.1.04,9]hexatriaconta-16,24,26,28-tetraene-2,3,10,14,20-pentone and (1R,9S,12S,15R,16Z,18R,19R,21R,23S,24E,26E,28E,30S,32S,35R)-1,18-Dihydroxy-12-[(2R)-1-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]propan-2-yl]-19,30-dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-hexamethyl-11,36-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[30.3.1.04,9]hexatriaconta-16,24,26,28-tetraene-2,3,10,14,20-pentone. Biological Half-Life ~30 hours. The mean elimination half-life of everolimus is approximately 30 hours. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Everolimus, an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase, is an antineoplastic agent and macrolide immunosuppressive agent. Everolimus (brand name Afinitor) is used in the treatment of certain types of breast cancers, neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin, renal cell carcinoma, renal angiomyolipoma with tuberous sclerosis complex, and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma with tuberous sclerosis complex. Everolimus (brand name Zortress) is used for the prophylaxis of organ rejection in adult patients at low-moderate immunologic risk receiving a kidney transplant. It is also used for the prophylaxis of allograft rejection in adult patients receiving a liver transplant. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Reported experience with overdose in humans is very limited. There is a single case of an accidental ingestion of 1.5 mg everolimus in a 2-year-old child where no adverse reactions were observed. Single doses up to 25 mg have been administered to transplant patients with acceptable acute tolerability. Single doses up to 70 mg (without cyclosporine) have been given with acceptable acute tolerability. Everolimus has immunosuppressive properties and may predispose patients to bacterial, fungal, viral, or protozoal infections, including opportunistic infections. Some of these infections have been severe (e.g., resulting in respiratory or hepatic failure) or fatal. Fatal noninfectious pneumonitis also has been reported with everolimus. Increases in serum creatinine concentrations and proteinuria have been reported in clinical trials with everolimus (Afinitor). Cases of renal failure (including acute renal failure), some with a fatal outcome, also have been observed in everolimus-treated patients. ANIMAL STUDIES: Everolimus was not carcinogenic in mice or rats when administered daily by oral gavage for 2 years at doses of 0.9 mg/kg. In animal reproductive studies, oral administration of everolimus to female rats before mating and through organogenesis induced embryo-fetal toxicities, including increased resorption, pre-implantation and post-implantation loss, decreased numbers of live fetuses, malformation (e.g., sternal cleft), and retarded skeletal development. These effects occurred in the absence of maternal toxicities. Embryo-fetal toxicities in rats occurred at doses greater than or equal to 0.1 mg/kg (0.6 mg/sq m). In rabbits, embryotoxicity evident as an increase in resorptions occurred at an oral dose of 0.8 mg/kg (9.6 mg/sq m. The effect in rabbits occurred in the presence of maternal toxicities. In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, animals were dosed from implantation through lactation. At the dose of 0.1 mg/kg (0.6 mg/sq m), there were no adverse effects on delivery and lactation or signs of maternal toxicity; however, there were reductions in body weight (up to 9% reduction from the control) and in survival of offspring (approximately 5% died or missing). There were no drug-related effects on the developmental parameters (morphological development, motor activity, learning, or fertility assessment) in the offspring. In a 13-week male fertility oral gavage study in rats, testicular morphology was affected at 0.5 mg/kg and above, and sperm motility, sperm head count and plasma testosterone concentrations were diminished at 5 mg/kg which caused a decrease in male fertility. There was evidence of reversibility of these findings in animals examined after 13 weeks post-dosing. The 0.5 mg/kg dose in male rats resulted in AUCs in the range of clinical exposures, and the 5 mg/kg dose resulted in AUCs approximately 5 times the AUCs in humans receiving 0.75 mg twice daily. Everolimus did not affect female fertility in nonclinical studies, but everolimus crossed the placenta and was toxic to the conceptus. Everolimus was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation, the mouse lymphoma thymidine kinase assay, or the chromosome aberration assay using V79 Chinese hamster cells, or in vivo following two daily doses of 500 mg/kg in the mouse micronucleus assay. Hepatotoxicity Serum enzyme elevations occur in up to a quarter of patients taking everolimus, but the abnormalities are usually mild, asymptomatic and self-limiting, rarely requiring dose modification or discontinuation. Liver test elevations above 5 times ULN occur in only 1% to 2% of treated patients. In contrast, idiosyncratic, clinically apparent acute liver injury has not been linked to everolimus therapy despite its wide scale use in several malignant and non-malignant syndromes. Elevations in serum enzymes and bilirubin and hepatitis are listed as potential adverse events in the product label for everolimun. Thus, acute clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice due to everolimus is probably quite rare, if it occurs at all. Importantly, everolimus is immunosuppressive and therapy in patients with cancer has been associated with episodes of reactivation of hepatitis B, which can be severe and even fatal. Reverse seroconversion (development of HBsAg in a person with preexisting antibody to hepatitis B, either anti-HBs or anti-HBc) has also been reported. Likelihood score: E* (unproven and also unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury but capable of inducing reactivation of hepatitis B). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation In two women, everolimus was either undetectable or detectable in very small amounts in the colostrum. However, no information is available on the use of everolimus during breastfeeding. An alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding ~ 74% in both healthy patients and those with moderate hepatic impairment. Interactions Use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors such as lovastatin or simvastatin was strongly discouraged in clinical trials of everolimus with cyclosporine in renal transplant patients because of an interaction between HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and cyclosporine. The manufacturer of Zortress recommends that patients receiving everolimus and cyclosporine therapy who are concurrently receiving an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor and/or fibric acid derivative be monitored for the possible development of rhabdomyolysis and other adverse effects, which are described in the prescribing information for these antilipemic agents. Studies in healthy individuals indicate that there are no clinically important pharmacokinetic interactions between single-dose everolimus and atorvastatin (a CYP3A4 substrate) or pravastatin (a non-CYP3A4 substrate and P-gp substrate); HMG-CoA reductase bioactivity in plasma also was not substantially affected. Therefore, dosage adjustments are not necessary when everolimus and atorvastatin or pravastatin are used concurrently. In a population pharmacokinetic analysis, simvastatin (a CYP3A4 substrate) did not affect clearance of everolimus. The manufacturer of Zortress cautions that these results cannot be extrapolated to other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Concomitant use of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors with everolimus may increase the risk of angioedema. The use of alternative antihypertensive agents should be considered in everolimus-treated patients, if necessary. If coadministration of a P-gp inhibitor is required in patients with SEGA, everolimus dosage should be reduced by approximately 50% to maintain trough everolimus concentrations of 5-10 ng/mL. If dosage reduction is required in patients receiving 2.5 mg daily, alternate-day dosing should be considered. Subsequent dosing should be individualized based on therapeutic drug monitoring. Trough everolimus concentrations should be assessed approximately 2 weeks after the addition of the P-gp inhibitor. If the P-gp inhibitor is discontinued, the everolimus dosage should be returned to the dosage used prior to initiation of the P-gp inhibitor and the trough everolimus concentration should be reassessed approximately 2 weeks later. For more Interactions (Complete) data for EVEROLIMUS (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| References |
|
| Additional Infomation |
Therapeutic Uses
Immunosuppressive Agents /CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health(NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Everolimus is included in the database. Afinitor is indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women with advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (advanced HR+ BC) in combination with exemestane, after failure of treatment with letrozole or anastrozole. /Included in US product label/ Afinitor Tablets and Afinitor Disperz are indicated in pediatric and adult patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) for the treatment of subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) that requires therapeutic intervention but cannot be curatively resected. /Included in US product label/c For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for EVEROLIMUS (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: MALIGNANCIES AND SERIOUS INFECTIONS. Only physicians experienced in immunosuppressive therapy and management of transplant patients should prescribe Zortress. Patients receiving the drug should be managed in facilities equipped and staffed with adequate laboratory and supportive medical resources. The physician responsible for maintenance therapy should have complete information requisite for the follow-up of the patient. Increased susceptibility to infection and the possible development of malignancies such as lymphoma and skin cancer may result from immunosuppression. /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: KIDNEY GRAFT THROMBOSIS. An increased risk of kidney arterial and venous thrombosis, resulting in graft loss, was reported, mostly within the first 30 days post-transplantation. /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: NEPHROTOXICITY. Increased nephrotoxicity can occur with use of standard doses of cyclosporine in combination with Zortress. Therefore reduced doses of cyclosporine should be used in combination with Zortress in order to reduce renal dysfunction. It is important to monitor the cyclosporine and everolimus whole blood trough concentrations. /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: MORTALITY IN HEART TRANSPLANTATION. Increased mortality, often associated with serious infections, within the first three months post-transplantation was observed in a clinical trial of de novo heart transplant patients receiving immunosuppressive regimens with or without induction therapy. Use in heart transplantation is not recommended. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for EVEROLIMUS (32 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| Molecular Formula |
C53H83NO14
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
958.22
|
| Exact Mass |
957.581
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 66.43; H, 8.73; N, 1.46; O, 23.38
|
| CAS # |
159351-69-6
|
| Related CAS # |
Everolimus-d4;1338452-54-2; Deprecated CAS 1245613-55-1
|
| PubChem CID |
6442177
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| Density |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| Boiling Point |
998.7±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| Melting Point |
NA
|
| Flash Point |
557.8±37.1 °C
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.548
|
| LogP |
3.35
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
14
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
9
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
68
|
| Complexity |
1810
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
15
|
| SMILES |
O=C1C([C@]2([C@@H](CC[C@@]([H])(C[C@@H](C(=CC=CC=C[C@H](C[C@H](C([C@@H]([C@@H](C(=C[C@H](C(C[C@]([H])(OC([C@]3([H])CCCCN31)=O)[C@H](C)C[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@@H](C1)OC)OCCO)=O)C)C)O)OC)=O)C)C)C)OC)O2)C)O)=O |t:11,13,15,23|
|
| InChi Key |
HKVAMNSJSFKALM-GKUWKFKPSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C53H83NO14/c1-32-16-12-11-13-17-33(2)44(63-8)30-40-21-19-38(7)53(62,68-40)50(59)51(60)54-23-15-14-18-41(54)52(61)67-45(35(4)28-39-20-22-43(66-25-24-55)46(29-39)64-9)31-42(56)34(3)27-37(6)48(58)49(65-10)47(57)36(5)26-32/h11-13,16-17,27,32,34-36,38-41,43-46,48-49,55,58,62H,14-15,18-26,28-31H2,1-10H3/b13-11+,16-12+,33-17+,37-27+/t32-,34-,35-,36-,38-,39+,40+,41+,43-,44+,45+,46-,48-,49+,53-/m1/s1
|
| Chemical Name |
(1R,9S,12S,15R,16E,18R,19R,21R,23S,24E,26E,28E,30S,32S,35R)-1,18- dihydroxy-12-{(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-(2hydroxyethoxy)-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethyl}-19,30-dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-hexamethyl-11,36-dioxa-4-aza-tricyclo[30.3.1.04,9]hexatriaconta16,24,26,28-tetraene-2,3,10,14,20-pentaone.
|
| Synonyms |
SDZ-RAD; RAD-001; RAD001; RAD 001; Everolimus; Brand name Afinitor; Certican; Zortress; Xience V; Zortress; 001, RAD; 40-O-(2-hydroxyethyl)-rapamycin; 40-O-(2-Hydroxyethyl)rapamycin; Afinitor; Certican; Everolimus; RAD;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.61 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (2.61 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.61 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 2.5 mg/mL (2.61 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 5: 2.5 mg/mL (2.61 mM) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 6: 30% Propylene glycol (dissolve first)+5% Tween 80+ddH2O: 5 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0436 mL | 5.2180 mL | 10.4360 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2087 mL | 1.0436 mL | 2.0872 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1044 mL | 0.5218 mL | 1.0436 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Sotorasib Activity in Subjects With Advanced Solid Tumors With KRAS p.G12C Mutation (CodeBreak 101)
CTID: NCT04185883
Phase: Phase 1 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-29
|
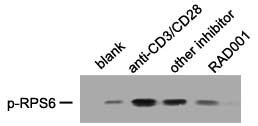 |
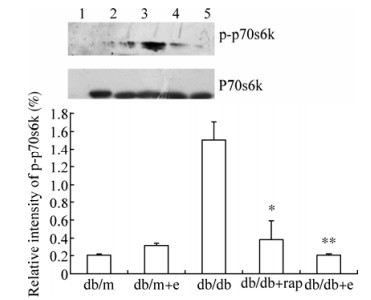 |