
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Gambogic Acid (also called Guttatic Acid, Guttic Acid) is a naturally occurring xanthonoid isolated from the brownish or orange resin from Garcinia hanburyi. It is presently undergoing clinical trials in China and may have antitumor properties. Gambogic acid works by competitively inhibiting Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, Bcl-W, Bcl-B, Bcl-B, and Mcl-1 with IC50 values of 1.47, 1.21, 2.02, 0.66, 1.06, and 0.79 μM, respectively. Caspases are activated by gambogic acid with an EC50 range of 0.78-1.64 μM. The cytotoxic natural substance GA blocks the ability of several antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members to suppress the release of apoptogenic proteins from mitochondria by competing for the BH3 peptide binding sites on these proteins. The proliferation of human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells was shown to be inhibited by GA in vitro in a dose-dependent manner. The rate of inhibition reached 89.45% after 72 hours of GA 5 mg/ml exposure to the cells.
| Targets |
Bcl-2 (Ki < 0.01 nM)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay |
Time-Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) Assays[1]
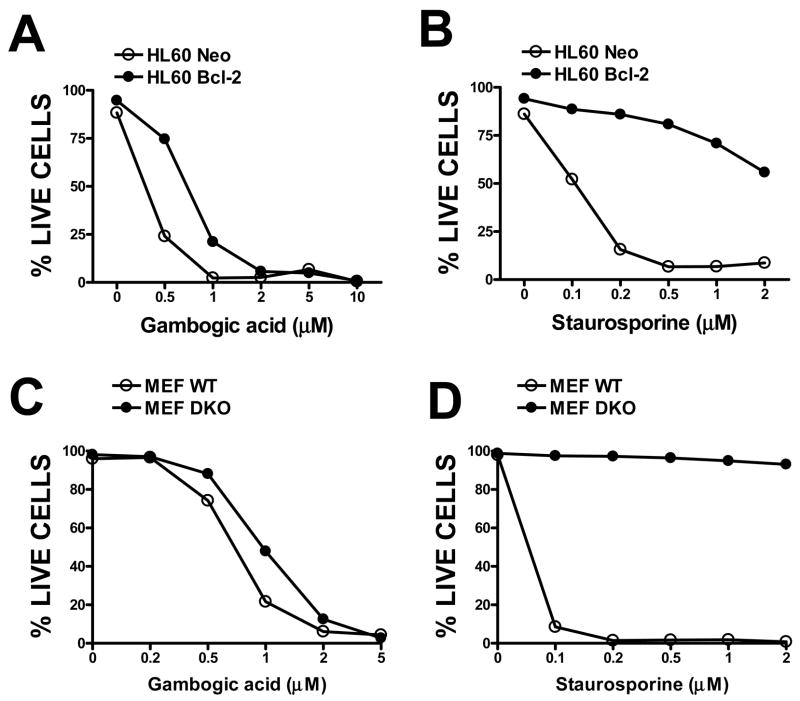
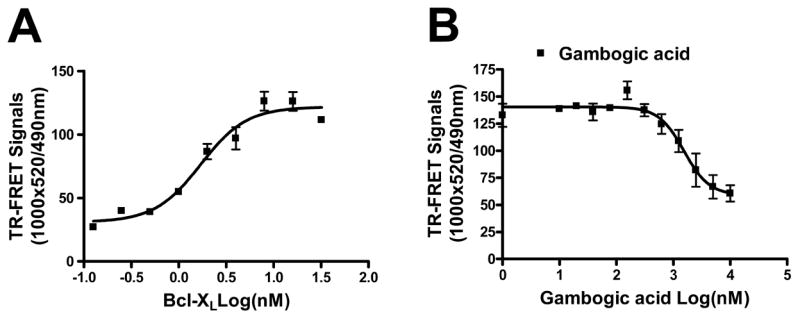
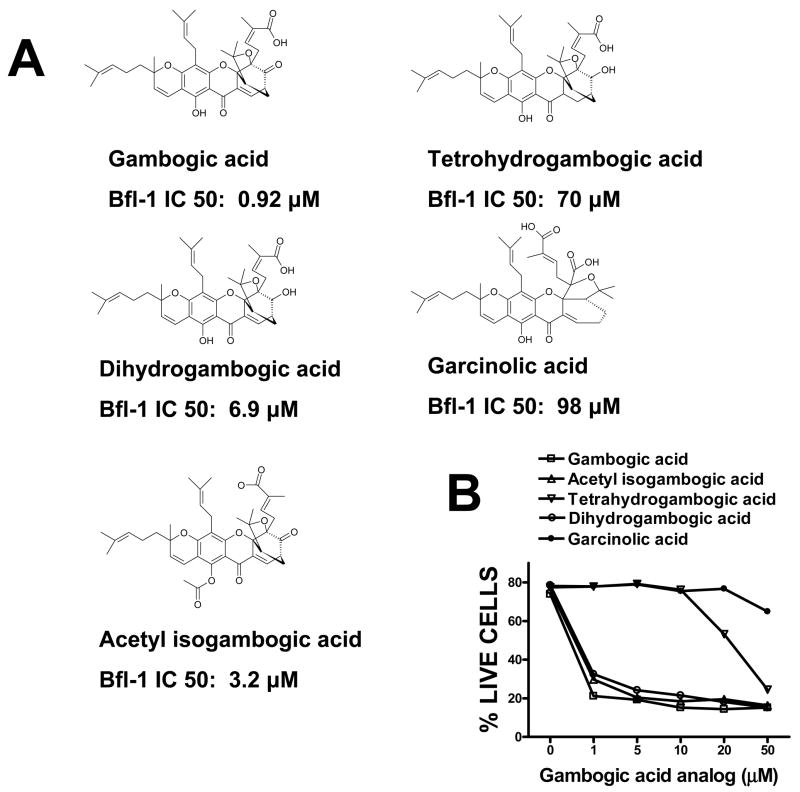
For TR-FRET assays, GST-Bcl-XL and anti-GST-terbium were mixed together with the FITC-Bad BH3 peptide in PBS containing 0.005% tween 20 in 96 well plates in a total volume of 20 μl per well. After incubation at room temperature for 30 min, 2 μl of gambogic acid-containing solutions were added to the reaction mixtures containing 10 nM of Bcl-XL, 10 nM of FITC-Bad BH3 peptide and 2 nM of anti-GST-terbium for 30 min at room temperature. TR-FRET signals were measured with a SpectraMax M5 plate reader using the following settings: excitation at 330nm, emission for FITC signal at 490 nm, and emission for terbium signal at 520 nm. Mitochondria Purification and Protein Release Assays[1] HeLa cells were pelleted by centrifugation, and then washed once in HM buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 250 mM mannitol, 10 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA), containing 1 mM PMSF and a mixture of protease inhibitors. The cell pellet was then homogenized in HM buffer by 50 strokes of a dounce homogenizer, using a B-type pestle. The homogenate was centrifuged twice at 600g for 5 min to remove nuclei and debris. The resulting supernatant was centrifuged at 10,000g for 10 min, and the resulting mitochondria-containing pellet was washed twice with the HM buffer.[1] For mitochondrial protein release assays, 10 μl of mitochondria (50 μg) were added into a final volume of 50 μl HM buffer containing gambogic acid, tBid or tBid pre-incubated with gambogic acid or Bcl-2 family proteins at 30°C for 15 min. The reactions were further incubated at 30°C for 40–60 min, then mitochondria were pelleted by centrifugation and the supernatants were collected, boiled in Laemmli sample buffer, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblotting using anti-SMAC antibody. The natural product gambogic acid (GA) has been reported to have cytotoxic activity against tumor cells in culture and was identified as an active compound in a cell-based high-throughput screening assay for activators of caspases, proteases involved in apoptosis. Using the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family protein, Bfl-1, as a target for screening of a library of natural products, we identified GA as a competitive inhibitor that displaced BH3 peptides from Bfl-1 in a fluorescence polarization assay. Analysis of competition for BH3 peptide binding revealed that GA inhibits all six human Bcl-2 family proteins to various extents, with Mcl-1 and Bcl-B the most potently inhibited [concentrations required for 50% inhibition (IC(50)), < 1 micromol/L]. Competition for BH3 peptide binding was also confirmed using a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. GA functionally inhibited the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins as shown by experiments using isolated mitochondria in which recombinant purified Bcl-2 family proteins suppress SMAC release in vitro, showing that GA neutralizes their suppressive effects on mitochondria in a concentration-dependent manner. GA killed tumor cell lines via an apoptotic mechanism, whereas analogues of GA with greatly reduced potency at BH3 peptide displacement showed little or no cytotoxic activity. However, GA retained cytotoxic activity against bax-/-bak-/- cells in which antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins lack a cytoprotective phenotype, implying that GA also has additional targets that contribute to its cytotoxic mechanism. Altogether, the findings suggest that suppression of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins may be among the cytotoxic mechanisms by which GA kills tumor cells.[1] gambogic acid (GA), a xanthone derived from the resin of the Garcinia hanburyi, has been recently demonstrated to bind transferrin receptor and exhibit potential anticancer effects through a signaling mechanism that is not fully understood. Because of the critical role of NF-kappaB signaling pathway, we investigated the effects of GA on NF-kappaB-mediated cellular responses and NF-kappaB-regulated gene products in human leukemia cancer cells. Treatment of cells with GA enhanced apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and chemotherapeutic agents, inhibited the expression of gene products involved in antiapoptosis (IAP1 and IAP2, Bcl-2, Bcl-x(L), and TRAF1), proliferation (cyclin D1 and c-Myc), invasion (COX-2 and MMP-9), and angiogenesis (VEGF), all of which are known to be regulated by NF-kappaB. GA suppressed NF-kappaB activation induced by various inflammatory agents and carcinogens and this, accompanied by the inhibition of TAK1/TAB1-mediated IKK activation, inhibited IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation, suppressed p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation, and finally abrogated NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene expression. The NF-kappaB activation induced by TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK, TAK1/TAB1, and IKKbeta was also inhibited. The effect of GA mediated through transferrin receptor as down-regulation of the receptor by RNA interference reversed its effects on NF-kappaB and apoptosis. Overall our results demonstrate that GA inhibits NF-kappaB signaling pathway and potentiates apoptosis through its interaction with the transferrin receptor.[3] |
|
| Cell Assay |
MTT assay is used to assess how treatments such as gambogic acid, CDDP alone, or both together, affect in vitro cell viability. In 96-well culture plates, the cells (2×104 cells per mL) are seeded. Following an overnight incubation, gambogic acid is applied to NCI-H460, A549, and NCI-H1299 cells in the following concentrations: 0.125, 0.25, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 μM, 0.44, 0.88, 1.75, 3.5, 7, 10.5 and 14 μM, and 0.44, 0.88, 1.75, 4, 8, 12, and 16 μM respectively. In NSCLC cells, three sequences are tested for the combined treatment: (a) Gambogic Acid followed by CDDP cells are exposed to Gambogic Acid for 48 h, and then after washout of Gambogic Acid, cells are treated with CDDP for an additional 48 h; (b) CDDP followed by Gambogic Acid cells are exposed to CDDP for 48 h, and then after washout of CDDP, cells are treated with Gambogic Acid for an additional 48 h; and (c) concurrent treatment cells are exposed to both Gambogic Acid and ADM for 48 h. The nature of the drug interaction is analysed by using the combination index (CI)[2].
|
|
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: A549 viable cells (5×106/100 μL PBS per mouse) are subcutaneously injected into the right flank of male SCID mice that are 7 to 8 weeks old in order to assess the in vivo antitumor activity of gambogic acid combined with CDDP. The mice are randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups when the tumor volume reaches 100 mm3, including control (saline only, n=5), gambogic acid (3.0 mg/kg every two days, intravenously; n=6), CDDP (4 mg/kg every week, intravenously; n=6), and sequential combination (CDDP treatment one day before gambogic acid treatment, n=6). To help detect any additive effects of combination therapy with platinum-based agents and gambogic acid, CDDP (4 mg/kg, weekly) is typically administered at doses lower than the maximum tolerated dose. Once every two days, a caliper is used to measure the tumor's size. Once every two days, body weight is measured. The tumors are removed after 14 days, and the mice are then put to death. They are then kept at -80°C for future research.
|
|
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
rat LD50 intraperitoneal 88 mg/kg LIVER: OTHER CHANGES Indian Journal of Experimental Biology., 5(96), 1967 [PMID:6062434]
rat LD50 intravenous 107 mg/kg LIVER: OTHER CHANGES Indian Journal of Experimental Biology., 5(96), 1967 [PMID:6062434] mouse LD50 subcutaneous 354 mg/kg CRC Handbook of Antibiotic Compounds, Vols.1- , Berdy, J., Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, 1980, 8(1)(331), 1982 mammal (species unspecified) LD50 unreported 55 mg/kg Zhongliu Yanjiu Cancer Review, Yu, R., et al., eds., Shanghai Science/Technology Publisher,Peop. Rep. China, 1994, -(220), 1994 |
|
| References | ||
| Additional Infomation |
beta-Guttiferin has been reported in Garcinia hanburyi with data available.
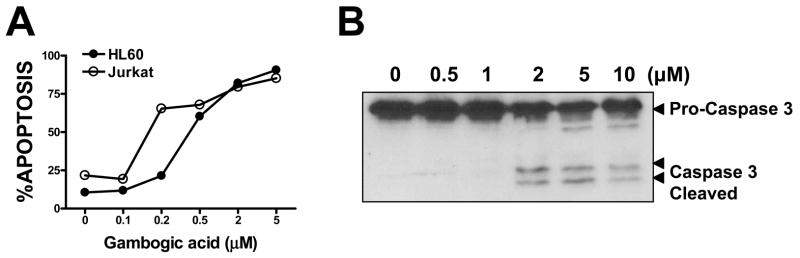
Gambogic acid (2), a natural product isolated from the resin of Garcinia hurburyi tree, was discovered to be a potent apoptosis inducer using our cell- and caspase-based high-throughput screening assays. Gambogic acid was found to have an EC(50) of 0.78 microM in the caspase activation assay in T47D breast cancer cells. The apoptosis-inducing activity of gambogic acid was further characterized by a nuclear fragmentation assay and flow cytometry analysis in human breast tumor cells T47D. Gambogic acid was found to induce apoptosis independent of cell cycle, which is different from paclitaxel that arrests cells in the G2/M phase. To understand the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of gambogic acid, derivatives of 2 with modifications to different function groups were prepared. SAR studies of gambogic acid, as measured by the caspase activation assay, showed that the 9,10 carbon-carbon double bond of the alpha,beta-unsaturated ketone is important for biological activity, while the 6-hydroxy and 30-carboxy group can tolerate a variety of modifications. The importance of the 9,10 carbon-carbon double bond was confirmed by the traditional growth inhibition assay. The high potency of 2 as an inducer of apoptosis, its novel mechanism of action, easy isolation and abundant supply, as well as the fact that it is amenable to chemical modification, makes gambogic acid an attractive molecule for the development of anticancer agents.[2] Gambogic acid (GA), the main active compound of Gamboge hanburyi, has been previously reported to activate apoptosis in many types of cancer cell lines by targeting transferrin receptor and modulating nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Whether GA inhibits angiogenesis, which is crucial for cancer and other human diseases, remains unknown. Here, we found that GA significantly inhibited human umbilical vascular endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation, migration, invasion, tube formation, and microvessel growth at nanomolar concentration. In a xenograft prostate tumor model, we found that GA effectively inhibited tumor angiogenesis and suppressed tumor growth with low side effects using metronomic chemotherapy with GA. GA was more effective in activating apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation and migration in HUVECs than in human prostate cancer cells (PC3), suggesting GA might be a potential drug candidate in cancer therapy through angioprevention with low chemotoxicity. Furthermore, we showed that GA inhibited the activations of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 and its downstream protein kinases, such as c-Src, focal adhesion kinase, and AKT. Together, these data suggest that GA inhibits angiogenesis and may be a viable drug candidate in antiangiogenesis and anticancer therapies. [4] Gambogic acid (GA) is a caged xanthone that is derived from Garcinia hanburyi and functions as a strong apoptotic inducer in many types of cancer cells. The distinct effectiveness of GA has led to its characterization as a novel anti-cancer agent. There is an increasing number of research studies focused on elucidating the molecular mechanisms of GA-induced anti-cancer effects, and several critical signaling pathways have been reported to be influenced by GA treatment. In this review, we summarize the multiple functional effects of GA administration in cancer cells including the induction of apoptosis, the inhibition of proliferation and the prevention of cancer metastasis and tumor angiogenesis. [5] |
| Molecular Formula |
C38H44O8
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
628.75
|
|
| Exact Mass |
628.303
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 72.59; H, 7.05; O, 20.36
|
|
| CAS # |
2752-65-0
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9852185
|
|
| Appearance |
Yellow solid powder
|
|
| Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
808.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Melting Point |
88.5°C
|
|
| Flash Point |
251.4±27.8 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.627
|
|
| LogP |
10.3
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
8
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
8
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
46
|
|
| Complexity |
1490
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
5
|
|
| SMILES |
O1C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C2([H])C([H])([H])C3([H])C([H])=C4C(C5C(=C6C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(\C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H])OC6=C(C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(\C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H])C=5OC24C1(C([H])([H])C([H])=C(C(=O)O[H])C([H])([H])[H])C3=O)O[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
GEZHEQNLKAOMCA-RRZNCOCZSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C38H44O8/c1-20(2)10-9-15-36(8)16-14-24-29(39)28-30(40)26-18-23-19-27-35(6,7)46-37(33(23)41,17-13-22(5)34(42)43)38(26,27)45-32(28)25(31(24)44-36)12-11-21(3)4/h10-11,13-14,16,18,23,27,39H,9,12,15,17,19H2,1-8H3,(H,42,43)/b22-13-/t23-,27+,36-,37+,38-/m1/s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
(Z)-4-[(1S,2S,8R,17S,19R)-12-hydroxy-8,21,21-trimethyl-5-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-8-(4-methylpent-3-enyl)-14,18-dioxo-3,7,20-trioxahexacyclo[15.4.1.02,15.02,19.04,13.06,11]docosa-4(13),5,9,11,15-pentaen-19-yl]-2-methylbut-2-enoic acid
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: 2% DMSO+40% PEG 300+2% Tween 80+ddH2O: 4mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5905 mL | 7.9523 mL | 15.9046 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3181 mL | 1.5905 mL | 3.1809 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1590 mL | 0.7952 mL | 1.5905 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
|
|---|
 |
 |
|---|
 |
 |