
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
(+)-JQ1 is a novel, potent and highly specific BET (Bromodomain and extra terminal domain) bromodomain inhibitor with antineoplastic activity. It inhibits BRD4(1/2) with an IC50 of 77 nM and 33 nM in enzymatic assays. It has high specificity for BET in that it only binds to bromodomains of the BET family, but not to any bromodomains of non-BET family. (+)-JQ1 has potential antineoplastic activity against various cancers such as MM (Multiple myeloma), pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and ovarian cancer etc. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit c-MYC and upregulate p21. (+)-JQ1 has been used as a chemical probe to investigate the role of BET bromodomains in the transcriptional regulation of oncogenesis.
| Targets |
BRD4 (1/2) (IC50= 77/33 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
(+)-JQ-1 represents a strong, highly selective and Kac-competitive inhibitor of the bromodomain BET family. (+)-JQ-1 (100 nM, 48 h) increases squamous development, evidenced by cell spindle formation, flattening, and enhanced keratin expression. (+)-JQ-1 (250 nM) stimulates fast expression of keratin in treated NMC 797 cells compared to (-)-JQ1 (250 nM) and vehicle control, as evaluated by quantitative immunohistochemistry of. (+)-JQ-1 (relative to (-)-JQ1 (250 nM)) causes time-dependent strong (3+) keratin staining in treated NMC 797 cells [1]. Derepression of autophagy genes was seen almost immediately upon addition of (+)-JQ-1 [2]. (+)-JQ-1 is a strong thiophenediazepine inhibitor (Kd=90 nM) of the BET family coactivator protein BRD4, which participates in the development of cancer through the transcriptional regulation of the MYC oncogene. Dose-ranging experiments of (+)-JQ-1 indicated efficient suppression of H4Kac4 binding, with IC50 values of 10 nM for mouse BRDT (1) and 11 nM for human BRDT (1) [3].
|
||
| ln Vivo |
Matching mouse cohorts with tumors that had already developed were randomized to receive intraperitoneal injections of either vehicle or (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) every day. FDG-PET imaging was used to assess the mice both four days post-treatment and before to randomization. FDG uptake was shown to be significantly reduced when (+)-JQ1 was administered. Tumor growth was inhibited by JQ1 treatment, as demonstrated by assessments of tumor volume. CD1 mice were used for pharmacokinetic studies of (+)-JQ1 following oral and intravenous dosing. Time profile of the mean plasma concentration of (+)-JQ1 following intravenous injection (5 mg/kg). The half-life (T1/2) of intravenous (+)-JQ1 was approximately one hour, and its pharmacokinetic characteristics demonstrated good drug exposure (AUC=2090 hr*ng/mL). After oral dosage (10 mg/kg), a mean plasma concentration-time profile of (+)-JQ1 was created. Oral (+)-JQ1 pharmacokinetic parameters showed good drug exposure (AUC=2090 hr*ng) /mL), peak plasma concentration (Cmax=1180 ng/mL), and oral bioavailability (F=49%)[1].
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
Acetyl-Histone Binding Assay. [1]
Assays were performed as described previously51 with minor modifications from the manufacturer’s protocol (PerkinElmer, USA). All reagents were diluted in 50 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 0.1 % BSA, pH 7.4 supplemented with 0.05 % CHAPS and allowed to equilibrate to room temperature prior to addition to plates. A 24-point 1:2 serial dilution of the ligands was prepared over the range of 150 – 0 μM and 4 μl transferred to low-volume 384-well plates, followed by 4 μl of His-tagged protein (BRD4(1), 250 nM, BRD4(2) and CREBBP, 2000 nM). Plates were sealed and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, before the addition of 4 μl of biotinylated peptide at equimolar concentration to the protein [peptide for BRD4(1) & BRD4(2): H4K5acK8acK12acK16ac, HSGRGK( Ac)GGK(Ac)GLGK(Ac)GGAK(Ac)RHRK(Biotin)-OH; peptide for CREBBP: H3K36ac, Biotin-KSAPATGGVK(Ac)KPHRYRPGT-OH]. Plates were sealed and incubated for a further 30 minutes, before the addition of 4 μl of streptavidin-coated donor beads (25 μg/ml) and 4 μl nickel chelate acceptor beads (25 μg/ml) under low light conditions. Plates were foil-sealed to protect from light, incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes and read on a PHERAstar FS plate reader using an AlphaScreen 680 excitation/570 emission filter set. IC50 values were calculated in Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, USA) after normalization against corresponding DMSO controls and are given as the final concentration of compound in the 20 μl reaction volume. |
||
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay. [1]
Cells were seeded into white, 384-well microtiter plates (Nunc) at 500 cells per well in a total volume of 50 μl media. The 797, TT and TE10 cells were grown in DMEM containing 1 % penicillin/streptomycin and 10 % FBS. The Per403 cells were grown in DMEM containing 1 % penicillin/streptomycin and 20 % FBS. Patient-derived NMC 11060 cells were grown in RPMI with 10 % FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Compounds were delivered to microtiter assay plates by robotic pin transfer (PerkinElmer JANUS equipped with a V&P Scientific 100 nl pin tool). Following a 48 h incubation at 37 ºC, cells were lysed and wells were assessed for total ATP content using a commercial proliferation assay. Replicate measurements were analyzed with respect to dose and estimates of IC50 were calculated by logistic regression. [1] Cell Growth Assay.[1] Cells were seeded in 6-well tissue culture dishes at a concentration of 1.5 x 104 cells per well. Cells were grown in 2 ml of either DMEM (797) or RPMI (11060) containing 10 % fetal bovine serum, 1 % penicillin/streptomycin and either 250 nM (+)-JQ1 or the equivalent volume of DMSO (0.025 %). One half of the media in each well was replaced daily. On days 0, 1, 3, 7 and 10, dishes of cells assigned to each time point were trypsinized, mixed in a 1:1 ratio with 0.4 % trypan blue and counted using a Countess automated cell counter. |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
JQ1 is a member of the class of thienotriazolodiazepines that is the tert-butyl ester of [(6S)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-trimethyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepin-6-yl]acetic acid. An inhibitor of bromodomain-containing protein 4 that exhibits anti-cancer and cardioprotective properties. It has a role as a bromodomain-containing protein 4 inhibitor, a cardioprotective agent, an antineoplastic agent, an anti-inflammatory agent, an angiogenesis inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer and a ferroptosis inducer. It is a thienotriazolodiazepine, an organochlorine compound, a carboxylic ester and a tert-butyl ester.
|
| Molecular Formula |
C23H25CLN4O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
456.99
|
|
| Exact Mass |
456.138
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 60.45; H, 5.51; Cl, 7.76; N, 12.26; O, 7.00; S, 7.02
|
|
| CAS # |
1268524-70-4
|
|
| Related CAS # |
(R)-(-)-JQ1 Enantiomer;1268524-71-5;JQ-1 (carboxylic acid);202592-23-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
46907787
|
|
| Appearance |
White to yellow solid
|
|
| Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| Boiling Point |
610.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| Flash Point |
322.9±34.3 °C
|
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.657
|
|
| LogP |
4.49
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
0
|
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
6
|
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
5
|
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
31
|
|
| Complexity |
706
|
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C1C2C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])SC=2N2C(C([H])([H])[H])=NN=C2[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C(=O)OC(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
DNVXATUJJDPFDM-KRWDZBQOSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H25ClN4O2S/c1-12-13(2)31-22-19(12)20(15-7-9-16(24)10-8-15)25-17(11-18(29)30-23(4,5)6)21-27-26-14(3)28(21)22/h7-10,17H,11H2,1-6H3/t17-/m0/s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 2% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O:5mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1882 mL | 10.9412 mL | 21.8823 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4376 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2188 mL | 1.0941 mL | 2.1882 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Leukemia and lymphoma cell lines are broadly sensitive to BET-bromodomain inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
Gene expression profiling of LP-1 and Raji cells treated with active or inactive BET inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
Small molecule BET-bromodomain inhibition suppressesMYCtranscription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
MYC reconstitution significantly protects cells from BET-mediated effects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
BET-bromodomain inhibition decreases tumor load in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
Integrated genomic rationale for BET bromodomains as therapeutic targets in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Inhibition of Myc-dependent transcription by theJQ1BET bromodomain inhibitor.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
BET inhibition suppressesMYCtranscription in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Regulation ofMYCtranscription by BET bromodomains.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Anti-myeloma activity ofJQ1in vitro.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
JQ1induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence in MM cells.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
Translational implications of BET bromodomain inhibition in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
|
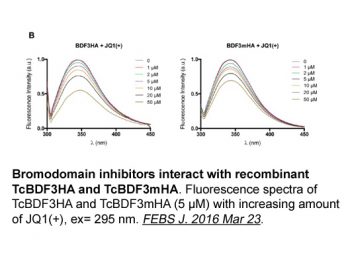 |
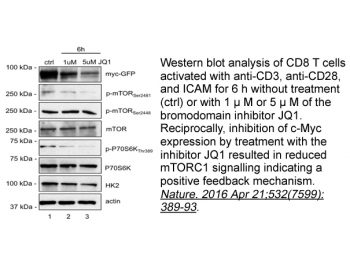 |