
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
LW6 is a hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF) inhibitor which potently inhibits HIF-1α accumulation by degrading HIF-1α without affecting the HIF-1a mRNA levels during hypoxia. It inhibits HIF-1α transcription activity with IC50 of 2.64 μM in cell-based HRE-reporter gene assays. LW6 decreases HIF-1α protein expression without affecting HIF-1β expression. LW6 affects the stability of the HIF-1α protein. LW6 promotes the degradation of wild type HIF-1α, but not of a DM-HIF-1α with modifications of P402A and P564A, at hydroxylation sites in the oxygen-dependent degradation domain. LW6 did not affect the activity of prolyl hydroxylase (PHD), but induced the expression of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL), which interacts with prolyl-hydroxylated HIF-1alpha for proteasomal degradation.
| ln Vitro |
The HIF-1α protein's stability is impacted by LW6. LW6 stimulates the hydroxylation sites in the oxygen-dependent degradation domain of wild type HIF-1α, but not that of a DM-HIF-1α with modifications of P402A and P564A. Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) is induced by LW6 and interacts with prolyl-hydroxylated HIF-1α to facilitate proteasomal degradation. HIF-1α protein accumulation is not eliminated by VHL knockdown in the presence of LW6, suggesting that HIF-1α was degraded by LW6 through control of VHL expression[2]. LW6 is known to significantly increase the cellular accumulation of mitoxantrone, a substrate of BCRP, in MDCKII-BCRP cells that overexpress BCRP. BCRP expression is also down-regulated by LW6 at 0.1–10 µM concentrations[3]. At 20 µM, LW6 suppresses the expression of HIF 1α in A549 cells that have been hypoxic, without requiring the von Hippel Lindau protein. In addition to lowering the potential of the mitochondrial membrane, LW6 causes hypoxia-selective apoptosis[4].
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vivo |
LW6 exhibits potent anti-tumor efficacy in vivo and reduces HIF-1α expression in frozen-tissue immunohistochemical staining in mice bearing xenografts of human colon cancer HCT116 cells[2].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Naik R, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship study of chemical probes as hypoxia induced factor-1α/malate dehydrogenase 2 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2014 Nov 26;57(22):9522-38.
[2]. Lee K, et al. LW6, a novel HIF-1 inhibitor, promotes proteasomal degradation of HIF-1alpha via upregulation of VHL in a colon cancer cell line. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Oct 1;80(7):982-9. [3]. Song JG, et al. Discovery of LW6 as a new potent inhibitor of breast cancer resistance protein. [4]. Sato M, et al. LW6, a hypoxia-inducible factor 1 inhibitor, selectively induces apoptosis in hypoxic cells through depolarization of mitochondria in A549 human lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):3462-8 |
| Molecular Formula |
C26H29NO5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
435.51
|
|
| Exact Mass |
435.2
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 71.70; H, 6.71; N, 3.22; O, 18.37
|
|
| CAS # |
934593-90-5
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| Appearance |
white solid powder
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(OC)C1=CC=C(O)C(NC(COC2=CC=C(C34CC5CC(C4)CC(C5)C3)C=C2)=O)=C1
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.5 mg/mL (5.74 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.74 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2962 mL | 11.4808 mL | 22.9616 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4592 mL | 2.2962 mL | 4.5923 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2296 mL | 1.1481 mL | 2.2962 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
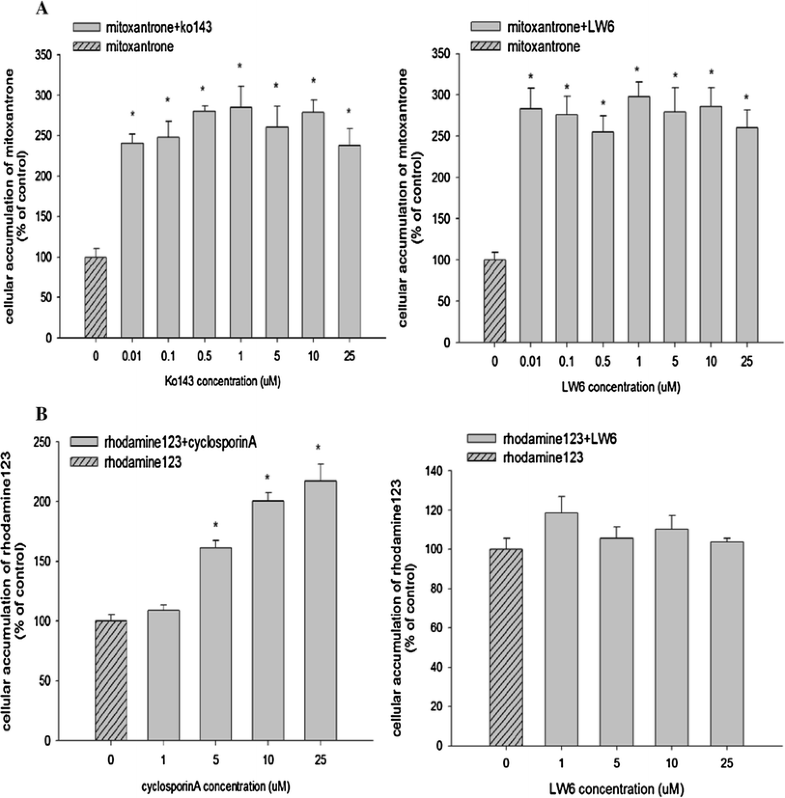 Inhibition effect of LW6 on the cellular accumulation of mitoxantrone in MDCKII-BCRP cells (a) and rhodamine-123 in MDCKII-MDR1 cells (b) (mean±SD,n=6). *pCancer Chemother Pharmacol.2016 Oct;78(4):735-44. |
|---|
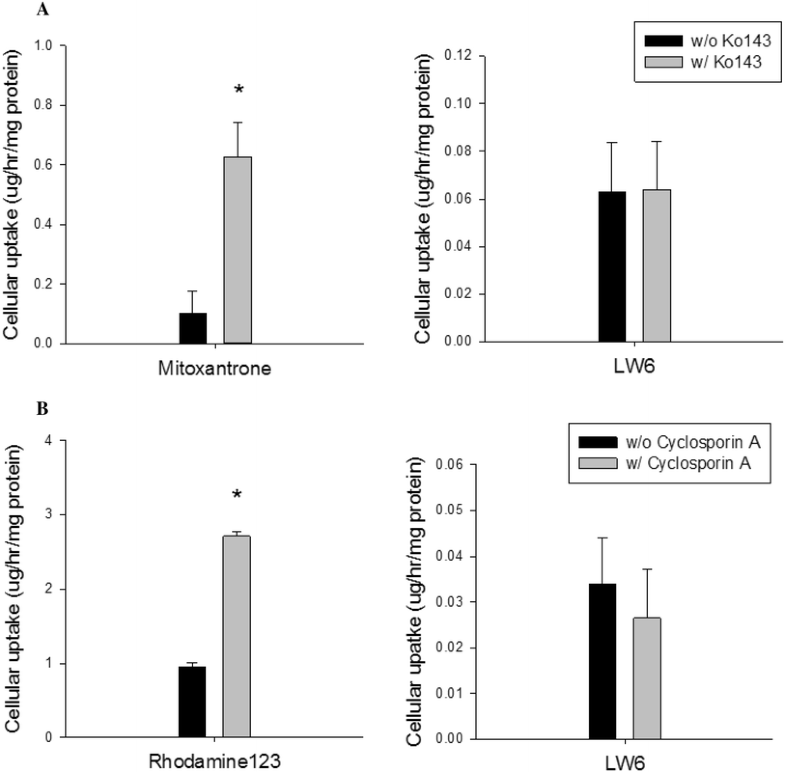 Cellular uptake studies of LW6 in MDCKII-BCRP cells (a) and MDCKII-MDR1 cells (b) (mean±SD,n=6).Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.2016 Oct;78(4):735-44. |
Effect of LW6 on the expression of BCRP.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.2016 Oct;78(4):735-44. |
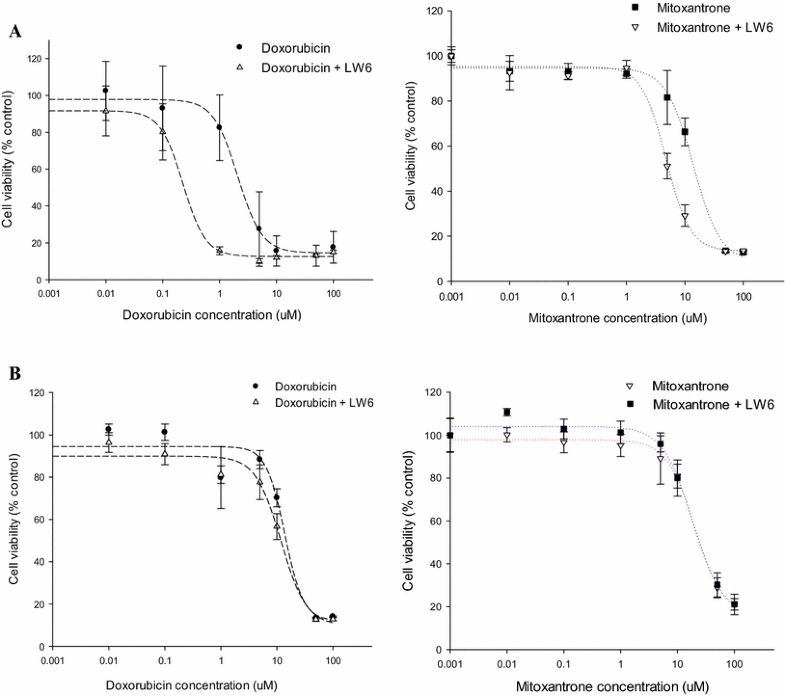 Cytotoxicity of mitoxantrone and doxorubicin with/without LW6 in MDCKII-BCRP.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.2016 Oct;78(4):735-44. |
|---|
Plasma concentration–time profiles of methotrexate after an oral administration of methotrexate (10mg/kg) in the presence and absence of LW6 (10mg/kg) in rats (mean±SD,n=5).Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.2016 Oct;78(4):735-44. |