
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
ML-161 is a novel and potent allosteric inhibitor of PAR1 (proteinase-activated receptor 1) on platelets with IC50 of 0.26 μM. ML161 exhibits a different selectivity with the reported ALK inhibitor crizotinib. ML161 treatment was found to inhibit the activation of thrombin-induced platelets in a dose-dependent manner through the detection of P-selectin expression in human platelets. ML161 demonstrated a significant suppression of P-selectin expression in a dose-dependent manner with an EC50 value of 0.3μM when tested with granule secretion. Additionally, it prevented SFLLRN-induced thrombus formation. With an IC50 value of 0.26 µM, ML-161 inhibits P-selectin'ssurfaceexpression that is induced by the peptide SFLLRN. When thrombin or a PAR1 peptide agonist were used to cause platelet aggregation, ML161 prevented it, but not when using multiple other platelet agonists.
| Targets |
PAR1 ( IC50 = 0.26 μM )
|
|
|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
Parmodulin 2 (ML161; 5 mg/kg; IV) significantly prevents platelet thrombus formation, with aa 73% reduction in AUC (area under the curve)[2].
Parmodulin 2 does not increase bleeding time; instead, it prevents platelet thrombus formation in vivo. Platelet aggregation is selectively inhibited by Parmodulin 2 via the α2A-adrenergic receptor and Par1[2]. |
|
| Enzyme Assay |
In order to determine possible targets of hit compounds, a high-throughput screen of the NIH-MLSMR compound collection and a number of secondary assays were used to find a 1,3-diaminobenzene scaffold that targets protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1). We hereby present further studies of the structure-activity relationship (SAR) that characterize the conditions for activity at PAR1 and pinpoint analogues that are stable in plasma that exhibit nanomolar inhibition of PAR1-mediated platelet activation. Compound 4 was declared as a probe (ML161) with the NIH Molecular Libraries Program. This substance prevented platelet aggregation brought on by thrombin or a PAR1 peptide agonist, but not by a number of other platelet agonists. According to preliminary research, ML161 is an allosteric inhibitor of PAR1. The identification of antithrombotics with an enhanced safety profile may benefit from these findings.
|
|
| Animal Protocol |
C57BL/6J wild type mice
5 mg/kg (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) IV |
|
| References |
| Molecular Formula |
C17H17BRN2O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
361.23
|
|
| Exact Mass |
360.05
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 56.52; H, 4.74; Br, 22.12; N, 7.75; O, 8.86
|
|
| CAS # |
423735-93-7
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| Appearance |
Solid powder
|
|
| SMILES |
CCCC(=O)NC1=CC(=CC=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2Br
|
|
| InChi Key |
DFOVLSMXPWPCFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H17BrN2O2/c1-2-6-16(21)19-12-7-5-8-13(11-12)20-17(22)14-9-3-4-10-15(14)18/h3-5,7-11H,2,6H2,1H3,(H,19,21)(H,20,22)
|
|
| Chemical Name |
2-bromo-N-[3-(butanoylamino)phenyl]benzamide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.92 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (6.92 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.92 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7683 mL | 13.8416 mL | 27.6832 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5537 mL | 2.7683 mL | 5.5366 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2768 mL | 1.3842 mL | 2.7683 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
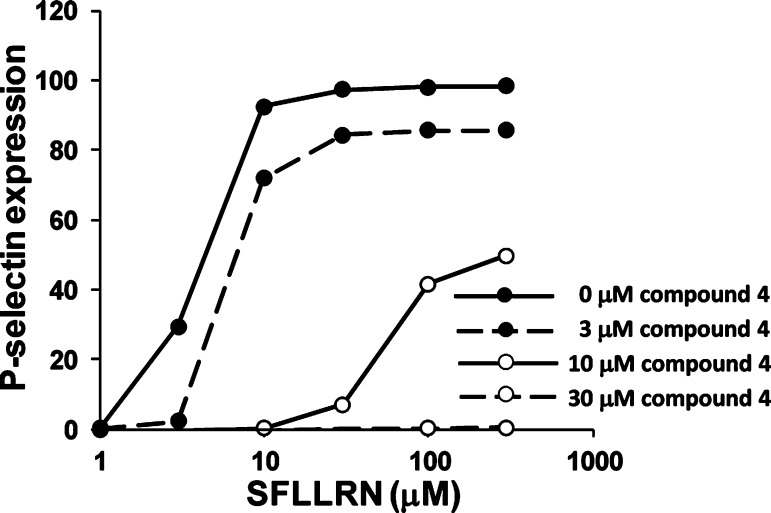 Dose–response curves of SFLLRN-induced P-selectin expression in the presence of varying concentrations of the PAR1 inhibitor4.ACS Med Chem Lett.2012 Mar 8;3(3):232-237. |
|---|
Synthesis of4(ML161).ACS Med Chem Lett.2012 Mar 8;3(3):232-237. |