
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Nitazoxanide (also known as NTZ; NSC 697855) is a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative and a broad spectrum antiprotozoal agent with IC50 for canine influenza virus ranges from 0.17 to 0.21 μM. It was approved for treating human protozoan infections. Nitazoxanide reduces parasite growth in cell culture by more than 90% with little evidence of drug-associated cytotoxicity. Nitazoxanide is a new thiazolide antiparasitic agent that shows excellent in vitro activity against a wide variety of protozoa and helminths. Nitazoxanide and its metabolite tizoxanide are more active in vitro than metronidazole against G. intestinalis, E. histolytica and T. vaginalis.
| ln Vitro |
Globally, the most frequent cause of persistent diarrhea is the flagellated protozoan Giardia lamblia[1].
With an IC50 of 2.4 μM, nitazoxanide has an impact on the growth of G. lamblia trophozoite in axenic culture[1]. |
|---|---|
| ln Vivo |
A variety of intestinal parasites, including Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, Trichomonas vaginalis, the apicomplexan Cryptosporidium parvum, and enteric bacteria that infect both humans and animals, are resistant to nitazoxanide's broad range of in vivo activity[1].
Mice infected with the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) strain have a lower mortality rate when given nitazoxanide (50, 75, or 100 mg/kg/day; intragastric administration for up to 25 days) and are protected against a lethal dose challenge of JEV[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: Giardia lamblia trophozoites were cultured in increasing numbers (103–106 parasites per well) in human cancer colon Caco2 cells.
Concentration: 30 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: When Nitazoxanide was not present and the initial inoculum density was 105 parasites per well, 70–90% of the trophozoites stayed adhered to the Caco2 cells for a duration of 24–48 hours.In the presence of 30 μM Nitazoxanide with an inoculum density of 105 trophozoites, the number of parasites still attached to Caco2 cells after 24 hours dropped to less than 20% of the control value. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal Model: JEV was injected intraperitoneally into female Chinese Kunming mice that were three weeks old and weighed between 12 and 14 grams.[2]
Dosage: 50, 75 or 100 mg/kg/day Administration: Administered intragastrically by gavage Result: 50 mg/kg/day, 75 mg/kg/day and 100 mg/kg/day led to 30%, 70% and 90% mice survival, respectively. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula |
C12H9N3O5S
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
307.28
|
| Exact Mass |
307.03
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 46.90; H, 2.95; N, 13.67; O, 26.03; S, 10.44
|
| CAS # |
55981-09-4
|
| Related CAS # |
Nitazoxanide-d4;1246819-17-9
|
| Appearance |
Solid powder
|
| SMILES |
CC(OC1=CC=CC=C1C(NC2=NC=C([N+]([O-])=O)S2)=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
YQNQNVDNTFHQSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H9N3O5S/c1-7(16)20-9-5-3-2-4-8(9)11(17)14-12-13-6-10(21-12)15(18)19/h2-6H,1H3,(H,13,14,17)
|
| Chemical Name |
[2-[(5-nitro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl]phenyl] acetate
|
| Synonyms |
NSC-697855; NTZ; NSC 697855;NSC697855;Nitazoxanide, Alinia, Colufase, Daxon, Nitazoxamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 61~100 mg/mL ( 198.51~325.44 mM )
|
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 3.25 mg/mL (10.58 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 32.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL of PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL of Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL of normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 3.25 mg/mL (10.58 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2544 mL | 16.2718 mL | 32.5436 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6509 mL | 3.2544 mL | 6.5087 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3254 mL | 1.6272 mL | 3.2544 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
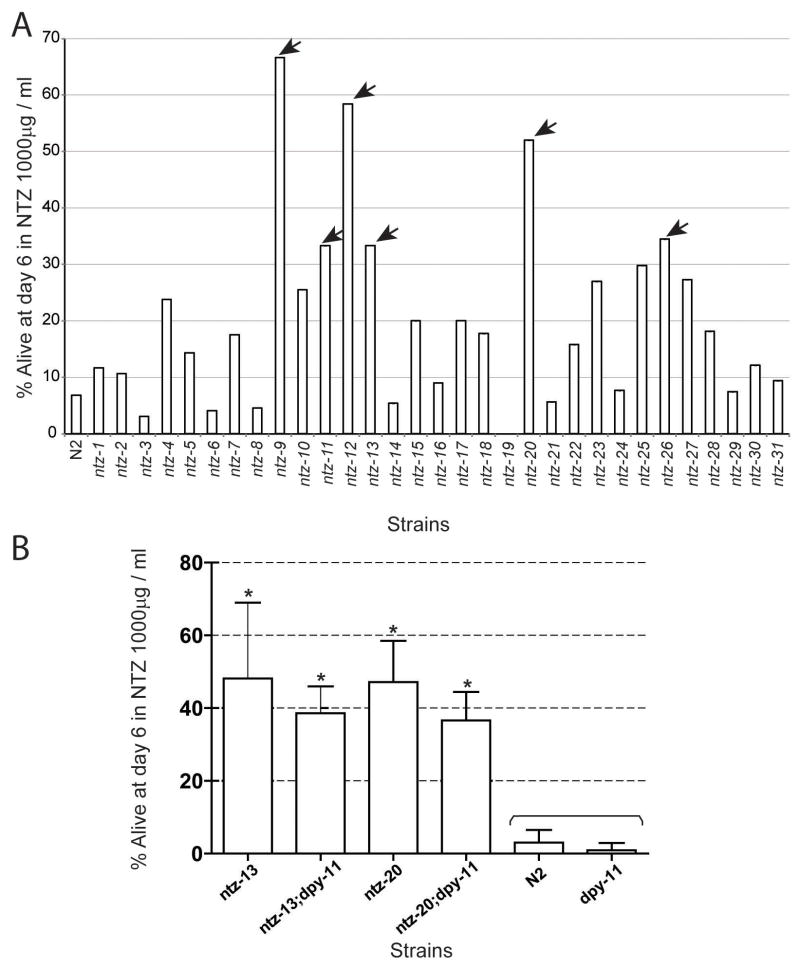 Forward genetic screen for identification of NTZ resistant worm mutants.Mol Biochem Parasitol.2014 Jan;193(1):1-8. |
|---|
Dose response curves ofC. elegansmutants resistant to other classes of drugs to NTZ in a six day lethality assay.Mol Biochem Parasitol.2014 Jan;193(1):1-8. |
Combination of NTZ with albendazole (ALB) and pyrantel (PYR).Mol Biochem Parasitol.2014 Jan;193(1):1-8. |
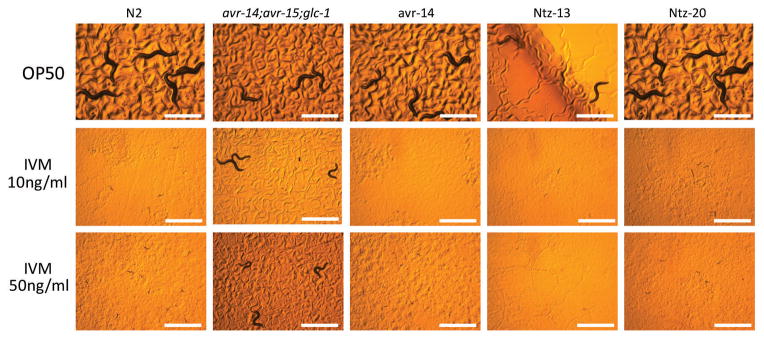 Ivermectin (IVM) susceptibility of the two NTZ resistant mutants identified in forward genetic screens at 44–45 hours.Mol Biochem Parasitol.2014 Jan;193(1):1-8. |
|---|
Effect of NTZ onC. elegansN2 wild-type nematodes.Mol Biochem Parasitol.2014 Jan;193(1):1-8. |