
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Paclitaxel (also known as NSC-125973; BMS-181339-01; trade name taxol; Anzatax; Asotax; Bristaxol) is a highly potent microtubule polymer stabilizer (mitotic inhibitor that stabilizes the polymerization of tubulin) with an IC50 of 0.1 pM in human endothelial cells. Paclitaxel has shown potent and a broad spectrum of antineoplastic activities, and has been extensively used in the treatment of various cancers. It is a natural product isolated from the Pacific yew tree Taxus brevifolia that has anticancer activity. Paclitaxel binds to tubulin and inhibits the disassembly of microtubules, thereby resulting in the inhibition of cell division. This agent also induces apoptosis by binding to and blocking the function of the apoptosis inhibitor protein Bcl-2.
| Targets |
Microtubule; tubulin polymerization; tubulin stabilizer
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
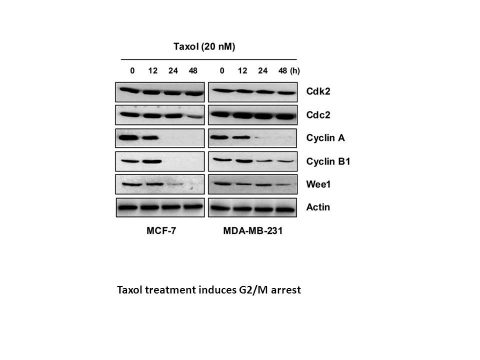
In the G2/M phase of the cell cycle, paclitaxel (20 nM; 48 h) causes programmed cell death and arrest [1]. A prolonged rise in p53 levels is induced by paclitaxel (20 nM; 48 hours). The anticancer agent, taxol, stabilizes tubulin polymerization, resulting in arrest at the G2/M phase of the cell cycle and apoptotic cell death. However, the molecular mechanism of this growth inhibition and apoptosis is poorly understood. In this study, we used MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells which have different estrogen receptor (ER) and tumor suppressor p53 statuses to examine the mechanisms of taxol-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. Treatment of the cells with taxol resulted in a time-dependent inhibition of cell viability, which was accompanied by an accumulation of cells at G2/M and the sub-G1 apoptotic region, determined by flow cytometric analysis. Furthermore, chromatin condensation, DNA ladder formation and proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in both cell lines were observed following treatment with taxol, indicating the occurrence of apoptotic cell death. Western blot analysis using whole cell lysates from MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells treated with taxol demonstrated that taxol treatment inhibited expression of cyclin A and cyclin B1 proteins in a time-dependent manner. The inhibitory effects of taxol on cell growth and apoptosis induced by taxol were also associated with the downregulation of Wee1 kinase expression and a marked induction in the activity of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21WAF/CIP1. Furthermore, taxol elevated p21 promoter activity in both cell lines. These findings suggest that taxol-induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells is mediated through the ER- and p53-independent upregulation of p21 [1].
Both tumor cell lines treated with pulsed paclitaxel exposures exhibited a significant number of cells undergoing apoptosis, however many fewer cells were arrested at the G2/M-phase of the cell cycle when compared to the continuous paclitaxel exposures. Short exposures to paclitaxel also induced the phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB-alpha, which in turn caused the activation of NF-kappaB in both cell lines. Parthenolide was found to inhibit paclitaxel-induced activation of the NF-kappaB/IkappaB signal pathway as well as apoptotic cell death. Conclusion: These findings suggest that paclitaxel-induced apoptosis might occur independent of a prior G2/M-phase arrest and be mediated or regulated by the NF-kappaB/IkappaB signal pathway[2]. To address the controversy regarding efficacy of paclitaxel in the presence of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, we investigated calcium stored in the endoplasmic reticulum as a potential factor. Our results showed that the ER calcium store is a common target for both paclitaxel and Bcl-2 protein. Paclitaxel directly associates with the endoplasmic reticulum to stimulate the release of calcium into the cytosol, contributing to the induction of apoptosis. However, Bcl-2 expression suppresses the cell's pro-apoptotic response of endoplasmic reticulum calcium release, thus inhibiting susceptibility of cancer cells to undergo apoptosis. Depending upon dosage, a paclitaxel-induced stimulatory effect can overcome the Bcl-2-mediated inhibitory effect on endoplasmic reticulum calcium release, thus attenuating the resistance of Bcl-2 to apoptosis. Our finding is the first to demonstrate that endoplasmic reticulum calcium plays a key role in the efficacy of paclitaxel in the presence of Bcl-2, thus providing insight into the complex but crucial paclitaxel-calcium-Bcl-2 relationship, which may impact breast cancer treatment[4]. |
| ln Vivo |
In the low-paclitaxel group, paclitaxel (1–20 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; once every two days, 5 cycles total) significantly increased the risk of liver metastasis while having minimal influence on the growth of the underlying tumor. Here we report that a low dose of paclitaxel enhances metastasis of breast cancer cells to the liver in mouse models. We used microarray analysis to investigate gene expression patterns in invasive breast cancer cells treated with low or clinically relevant high doses of paclitaxel. We also investigated the effects of low doses of paclitaxel on cell migration, invasion and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that low doses of paclitaxel promoted inflammation and initiated the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, which enhanced tumor cell migration and invasion in vitro. These effects could be reversed by inhibiting NF-κB. Furthermore, low doses of paclitaxel promoted liver metastasis in mouse xenografts, which correlated with changes in estrogen metabolism in the host liver. Collectively, these findings reveal the paradoxical and dose-dependent effects of paclitaxel on breast cancer cell activity, and suggest that increased consideration be given to potential adverse effects associated with low concentrations of paclitaxel during treatment [3].
The purpose of the present study was to test the prediction that the unique manifestation of chemotherapeutic-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) would be reflected in a specific pattern of changes in the regulation of the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i) in subpopulations of cutaneous neurons. To test this prediction, we characterized the pattern of changes in mechanical nociceptive threshold associated with paclitaxel administration (2mg/kg, iv, every other day for four days), as well as the impact of target of innervation and paclitaxeltreatment on the regulation of [Ca(2+)]i in subpopulations of putative nociceptive and non-nociceptive neurons. Neurons innervating the glabrous and hairy skin of the hindpaw as well as the thigh were identified with retrograde tracers, and fura-2 was used to assess changes in [Ca(2+)]i. Paclitaxel was associated with a persistent decrease in mechanical nociceptive threshold in response to stimuli applied to the glabrous skin of the hindpaw, but not the hairy skin of the hindpaw or the thigh. However, in both putative nociceptive and non-nociceptive neurons, resting [Ca(2+)]i was significantly lower in neurons innervating the thigh after treatment. The magnitude of the depolarization-evoked Ca(2+) transient was also lower in putative non-nociceptive thigh neurons. More interestingly, while paclitaxel had no detectable influence on either resting or depolarization-evoked Ca(2+) transients in putative non-nociceptive neurons, in putative nociceptive neurons there was a subpopulation-specific decrease in the duration of the evoked Ca(2+) transient that was largely restricted to neurons innervating the glabrous skin. These results suggest that peripheral nerve length alone, does not account for the selective distribution of CIPN symptoms. Rather, they suggest the symptoms of CIPN reflect an interaction between the toxic actions of the therapeutic and unique properties of the neurons deleteriously impacted[6]. |
| Enzyme Assay |
In Vitro Tubulin Polymerization Assay[8]
Tubulin was prepared as described before. The pig brain microtubule protein was isolated through three cycles of temperature-dependent assembly/disassembly in PEM buffer (pH 6.5, 100 mM PIPES, 2 mM EGTA, and 1 mM MgSO4) containing 1 mM GTP and 1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol. Tubulin was prepared from the microtubule protein by phosphocellulose chromatography and stored at −70 °C. Tubulin was mixed with indicated concentrations of test compounds in PEM buffer (100 mM PIPES, 1 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM EGTA) containing 1 mM GTP and 5% glycerol. Microtubule polymerization was monitored by a spectrophotometer at 340 nm. The plateau absorbance values were used for calculations. |
| Cell Assay |
Apoptosis Analysis[1]
Cell Types: MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 cells Tested Concentrations: 20 nM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced programmed cell death. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Types: MCF-7, MDA-MB -231 cells Tested Concentrations: 20 nM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: >60% of MCF-7 cells and 50% of MDA-MB-231 cells were in the G2/M phase following 24 h treament. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: MCF-7 cells (harboring wild-type p53) Tested Concentrations: 20 nM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced a consistent increase in the level of p53. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: MDA-231 xenograft-bearing mice[3]
Doses: 1, 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection; five cycles (1 time/2 days) Experimental Results: Liver metastases were obviously induced in the low-PTX (1 mg /kg) group with little influence on primary tumor growth compared with high-PTX group.《hr Paclitaxel treatment[6] One week following the DiI injection, rats were anesthetized with isofluorane and injected into the tail vein with 2 mg/kg paclitaxel or its vehicle (1:1:23, cremophor EL:ethanol:0.9% saline). The tail vein injection was repeated three more times every other day for a total of four injections. Primary tumor growth and metastasis detection in vivo[3] Specific pathogen free (SPF) nude mice were used. MDA-231 cells (1 × 106) were subcutaneously transplanted. After the formation of primary tumors (diameter > 5 mm), the mice were randomly grouped (10 mice per group) and different doses of PTX (paclitaxel) were diluted with normal saline and administrated by intraperitoneal injection (1 time/2 days). After five cycles of treatment, the mice were euthanized. The primary tumor growth and metastatic intensities were then measured, and images were captured. |
| References |
[1]. Choi YH, et al. Paclitaxel-induced growth arrest and apoptosis is associated with the upregulation of the Cdk inhibitor, p21WAF1/CIP1, in human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2012 Dec;28(6):2163-9.
[2]. Dziadyk JM, et al. Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis may occur without a prior G2/M-phase arrest. Anticancer Res. 2004 Jan-Feb;24(1):27-36. [3]. Li Q, et al. Low doses of paclitaxel enhance liver metastasis of breast cancer cells in the mouse model. FEBS J. 2016 Aug;283(15):2836-52. [4]. Pan Z, et al. Paclitaxel attenuates Bcl-2 resistance to apoptosis in breast cancer cells through an endoplasmic reticulum-mediated calciumrelease in a dosage dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Feb 13. pii: S0006-291X(13)00259-3. [5]. Cadamuro M, et al. Low dose paclitaxel reduces S100A4 nuclear import to inhibit invasion and hematogenous metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 21. [6]. Yilmaz E, et al. Sensory neuron subpopulation-specific dysregulation of intracellular calcium in a rat model of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience. 2015 Aug 6;300:210-8. [7]. Jing C, et al. E7080 enhances the antitumor effects of paclitaxel in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 1;7(4):903-912. [8]. X-ray Crystal Structure-Guided Discovery of Novel Indole Analogues as Colchicine-Binding Site Tubulin Inhibitors with Immune-Potentiating and Antitumor Effects against Melanoma. J Med Chem . 2023 May 25;66(10):6697-6714. |
| Additional Infomation |
Taxol appears as needles (from aqueous methanol) or fine white powder. An anti-cancer drug.
CAMEO Chemicals
Paclitaxel is a tetracyclic diterpenoid isolated originally from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia. It is a mitotic inhibitor used in cancer chemotherapy. Note that the use of the former generic name 'taxol' is now limited, as Taxol is a registered trade mark. It has a role as a microtubule-stabilising agent, a metabolite, a human metabolite and an antineoplastic agent. It is a tetracyclic diterpenoid and a taxane diterpenoid. It is functionally related to a baccatin III. ChEBI Paclitaxel is a chemotherapeutic agent marketed under the brand name Taxol among others. Used as a treatment for various cancers, paclitaxel is a mitotic inhibitor that was first isolated in 1971 from the bark of the Pacific yew tree which contains endophytic fungi that synthesize paclitaxel. It is available as an intravenous solution for injection and the newer formulation contains albumin-bound paclitaxel marketed under the brand name Abraxane. DrugBank Paclitaxel is a Microtubule Inhibitor. The physiologic effect of paclitaxel is by means of Microtubule Inhibition. FDA Pharm Classes Paclitaxel is an antineoplastic agent which acts by inhibitor of cellular mitosis and which currently plays a central role in the therapy of ovarian, breast, and lung cancer. Therapy with paclitaxel has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations, but has not been clearly linked to cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury. LiverTox Paclitaxel is a natural product found in Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis, Aspergillus versicolor, and other organisms with data available. LOTUS - the natural products occurrence database View MorePaclitaxel is a compound extracted from the Pacific yew tree Taxus brevifolia with antineoplastic activity. Paclitaxel binds to tubulin and inhibits the disassembly of microtubules, thereby resulting in the inhibition of cell division. This agent also induces apoptosis by binding to and blocking the function of the apoptosis inhibitor protein Bcl-2 (B-cell Leukemia 2). (NCI04) NCI Thesaurus (NCIt) Paclitaxel can cause developmental toxicity, female reproductive toxicity and male reproductive toxicity according to state or federal government labeling requirements. A cyclodecane isolated from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, TAXUS brevifolia. It stabilizes microtubules in their polymerized form leading to cell death. ABI-007 (Abraxane) is the latest attempt to improve upon paclitaxel, one of the leading chemotherapy treatments. Both drugs contain the same active agent, but Abraxane is delivered by a nanoparticle technology that binds to albumin, a natural protein, rather than the toxic solvent known as Cremophor. It is thought that delivering paclitaxel with this technology will cause fewer hypersensitivity reactions and possibly lead to greater drug uptake in tumors. Paclitaxel is a mitotic inhibitor used in cancer chemotherapy. It was discovered in a US National Cancer Institute program at the Research Triangle Institute in 1967 when Monroe E. Wall and Mansukh C. Wani isolated it from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia and named it taxol. Later it was discovered that endophytic fungi in the bark synthesize paclitaxel. Used in the treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma and cancer of the lung, ovarian, and breast. Abraxane® is specfically indicated for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer and locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Paclitaxel is an antineoplastic agent which acts by inhibitor of cellular mitosis and which currently plays a central role in the therapy of ovarian, breast, and lung cancer. Therapy with paclitaxel has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations, but has not been clearly linked to cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Standard formulation paclitaxel requires the use of solvents, such as Cremphor-EL, which contribute to some of the toxicities commonly associated with paclitaxel-based therapy. Nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel) is a novel solvent-free formulation of paclitaxel. The formulation is prepared by high-pressure homogenization of paclitaxel in the presence of serum albumin into a nanoparticle colloidal suspension. The human albumin-stabilized paclitaxel particles have an average size of 130 nm. Nab-paclitaxel has several practical advantages over Cremphor-EL-paclitaxel, including a shorter infusion time (30 min) and no need for premedications for hypersensitivity reactions. The nab-paclitaxel formulation eliminates the impact of Cremphor-EL on paclitaxel pharmacokinetics and utilizes the endogenous albumin transport mechanisms to concentrate nab-paclitaxel within the tumor. A recent Phase III trial compared nab- and Cremphor-EL-paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Patients treated with nab-paclitaxel experienced a higher response, longer time to tumor progression and, in patients receiving second-line or greater therapy, a longer median survival. Patients treated with nab-paclitaxel had a significantly lower rate of severe neutropenia and a higher rate of sensory neuropathy. The preclinical and clinical data indicate that the nab-paclitaxel formulation has significant advantages over Cremphor-EL-paclitaxel. Paclitaxel is a taxoid antineoplastic agent indicated as first-line and subsequent therapy for the treatment of advanced carcinoma of the ovary, and other various cancers including breast cancer. Paclitaxel is a novel antimicrotubule agent that promotes the assembly of microtubules from tubulin dimers and stabilizes microtubules by preventing depolymerization. This stability results in the inhibition of the normal dynamic reorganization of the microtubule network that is essential for vital interphase and mitotic cellular functions. In addition, paclitaxel induces abnormal arrays or "bundles" of microtubules throughout the cell cycle and multiple asters of microtubules during mitosis. Absorption: When a 24 hour infusion of 135 mg/m^2 is given to ovarian cancer patients, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is 195 ng/mL, while the AUC is 6300 ng•h/mL. Route of Elimination: In 5 patients administered a 225 or 250 mg/m2 dose of radiolabeled paclitaxel as a 3-hour infusion, a mean of 71% of the radioactivity was excreted in the feces in 120 hours, and 14% was recovered in the urine. Volume of Distribution: 227 to 688 L/m^2 [apparent volume of distribution at steady-state, 24 hour infusion] Clearance: 21.7 L/h/m2 [Dose 135 mg/m2, infusion duration 24 h] 23.8 L/h/m2 [Dose 175 mg/m2, infusion duration 24 h] 7 L/h/m2 [Dose 135 mg/m2, infusion duration 3 h] 12.2 L/h/m2 [Dose 175 mg/m2, infusion duration 3 h] Paclitaxel bound to nanoparticles of the serum protein albumin is delivered via endothelial transport mediated by albumin receptors, and the resulting concentration of paclitaxel in tumor cells is increased compared with that achieved using an equivalent dose of conventional paclitaxel. Like conventional paclitaxel, albumin-bound paclitaxel has a large volume of distribution. Following 30-minute or 3-hour IV infusion of 80-375 mg/sq m albumin-bound paclitaxel, the volume of distribution averaged 632 L/sq m. The volume of distribution of albumin-bound paclitaxel 260 mg/sq m by 30-minute IV infusion was 53% larger than the volume of distribution of conventional paclitaxel 175 mg/sq m by 3-hour IV infusion. /Paclitaxel (albumin-bound)/. Hepatic. In vitro studies with human liver microsomes and tissue slices showed that paclitaxel was metabolized primarily to 6a-hydrox-ypaclitaxel by the cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2C8; and to two minor metabolites, 3’-p-hydroxypaclitaxel and 6a, 3’-p-dihydroxypaclitaxel, by CYP3A4. Biological Half-Life: When a 24 hour infusion of 135 mg/m^2 is given to ovarian cancer patients, the elimination half=life is 52.7 hours. Paclitaxel interferes with the normal function of microtubule growth. Whereas drugs like colchicine cause the depolymerization of microtubules in vivo, paclitaxel arrests their function by having the opposite effect; it hyper-stabilizes their structure. This destroys the cell's ability to use its cytoskeleton in a flexible manner. Specifically, paclitaxel binds to the β subunit of tubulin. Tubulin is the "building block" of mictotubules, and the binding of paclitaxel locks these building blocks in place. The resulting microtubule/paclitaxel complex does not have the ability to disassemble. This adversely affects cell function because the shortening and lengthening of microtubules (termed dynamic instability) is necessary for their function as a transportation highway for the cell. Chromosomes, for example, rely upon this property of microtubules during mitosis. Further research has indicated that paclitaxel induces programmed cell death (apoptosis) in cancer cells by binding to an apoptosis stopping protein called Bcl-2 (B-cell leukemia 2) and thus arresting its function. Evidence suggests that paclitaxel also may induce cell death by triggering apoptosis. In addition, paclitaxel and docetaxel enhance the effects of ionizing radiation, possibly by blocking cells in the G2 phase, the phase of the cell cycle in which cells are most radiosensitive. Paclitaxel is an antimicrotubule antineoplastic agent. Unlike some other common antimicrotubule agents (e.g., vinca alkaloids, colchicine, podophyllotoxin), which inhibit microtubule assembly, paclitaxel and docetaxel (a semisynthetic taxoid) promote microtubule assembly. Microtubules are organelles that exist in a state of dynamic equilibrium with their components, tubulin dimers. They are an essential part of the mitotic spindle and also are involved in maintenance of cell shape and motility, and transport between organelles within the cell. By binding in a reversible, concentration-dependent manner to the beta-subunit of tubulin at the N-terminal domain, paclitaxel enhances the polymerization of tubulin, the protein subunit of the spindle microtubules, even in the absence of factors that are normally required for microtubule assembly (e.g., guanosine triphosphate [GTP]), and induces the formation of stable, nonfunctional microtubules. Paclitaxel promotes microtubule stability even under conditions that typically cause depolymerization in vitro (e.g., cold temperature, the addition of calcium, the presence of antimitotic drugs). While the precise mechanism of action of the drug is not understood fully, paclitaxel disrupts the dynamic equilibrium within the microtubule system and blocks cells in the late G2 phase and M phase of the cell cycle, inhibiting cell replication. |
| Molecular Formula |
C47H51NO14
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
853.91
|
| Exact Mass |
853.33093
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 66.11; H, 6.02; N, 1.64; O, 26.23
|
| CAS # |
33069-62-4
|
| Related CAS # |
Paclitaxel-d5;1129540-33-5;Paclitaxel-d5 (benzoyloxy);1261254-56-1; 33069-62-4; 186040-50-6 (ceribate); 263351-82-2 (Poliglumex); 117527-50-1 (Paclitaxel-Succinic acid)
|
| PubChem CID |
36314
|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| Density |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| Boiling Point |
957.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| Melting Point |
213 °C
|
| Flash Point |
532.6±34.3 °C
|
| Vapour Pressure |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| Index of Refraction |
1.637
|
| LogP |
7.38
|
| tPSA |
221.29
|
| SMILES |
O=C1[C@H](OC(C)=O)C(C2(C)C)=C(C)[C@@H](OC([C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(C3=CC=CC=C3)=O)C4=CC=CC=C4)=O)C[C@@]2(O)[C@@H](OC(C5=CC=CC=C5)=O)[C@@]6([H])[C@@]1(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]7([H])OC[C@]76OC(C)=O
|
| InChi Key |
RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C47H51NO14/c1-25-31(60-43(56)36(52)35(28-16-10-7-11-17-28)48-41(54)29-18-12-8-13-19-29)23-47(57)40(61-42(55)30-20-14-9-15-21-30)38-45(6,32(51)22-33-46(38,24-58-33)62-27(3)50)39(53)37(59-26(2)49)34(25)44(47,4)5/h7-21,31-33,35-38,40,51-52,57H,22-24H2,1-6H3,(H,48,54)/t31-,32-,33+,35-,36+,37+,38-,40-,45+,46-,47+/m0/s1
|
| Chemical Name |
(2aR,4S,4aS,6R,9S,11S,12S,12aR,12bS)-9-(((2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl)oxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-4,11-dihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-1H-7,11-methanocyclodeca[3,4]benzo[1,2-b]oxete-6,12b-diyl diacetate
|
| Synonyms |
NSC 125973; BMS 181339-01; NSC-125973; BMS181339-01; NSC125973; BMS-181339-01; Trade name: Taxol; Taxol Konzentrat; Anzatax; Asotax; Bristaxol; Praxel; TAX.P88XT4IS4D; Paclitaxel; Taxol A; Yewtaxan; Genaxol; Plaxicel;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (2.44 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.08 mg/mL (2.44 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (2.44 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 1% DMSO +30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 : 30 mg/mL Solubility in Formulation 5: 10 mg/mL (11.71 mM) in Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Solubility in Formulation 6: 10 mg/mL (11.71 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1711 mL | 5.8554 mL | 11.7108 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2342 mL | 1.1711 mL | 2.3422 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1171 mL | 0.5855 mL | 1.1711 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
|