
| Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
Palbociclib orotate (PD0332991; PD-0332991; brand name Ibrance) is an orally bioavailable pyridopyrimidine-based CDK4/6 inhibitor approved for cancer treatment. It inhibits CDK4/6 with IC50 of 11 nM and 16 nM in cell-free assays respectively. CDK4 and CDK6 are overexpressed in many tumor cells, and palbociclib, developed by Pfizer, is the first CDK4/6 inhibitor approved by FDA in 2017 as a cancer therapeutic. It shows no activity against CDK1/2/5, EGFR, FGFR, PDGFR, InsR, etc. It is a potent anti-proliferative agent against Rb-positive tumor cells in vitro, subsequently inducing an exclusive G1 arrest. It has been reported to prevent tumor growth in disseminated human myeloma xenografts and induce G1 arrest in primary bone marrow cells.
| Targets |
DYRK1A (IC50 = 2000 nM); MAPK (IC50 = 8000 nM); Cdk4/cyclin D3 (IC50 = 9 nM); Cdk4/cyclin D1 (IC50 = 11 nM); Cdk6/cyclin D2 (IC50 = 16 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
Palbociclib is a CDK4/6 inhibitor approved for metastatic estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. In addition to G1 cell cycle arrest, palbociclib treatment results in cell senescence, a phenotype that is not readily explained by CDK4/6 inhibition. In order to identify a molecular mechanism responsible for palbociclib-induced senescence, we performed thermal proteome profiling of MCF7 breast cancer cells. In addition to affecting known CDK4/6 targets, palbociclib induces a thermal stabilization of the 20S proteasome, despite not directly binding to it. We further show that palbociclib treatment increases proteasome activity independently of the ubiquitin pathway. This leads to cellular senescence, which can be counteracted by proteasome inhibitors. Palbociclib-induced proteasome activation and senescence is mediated by reduced proteasomal association of ECM29. Loss of ECM29 activates the proteasome, blocks cell proliferation, and induces a senescence-like phenotype. Finally, we find that ECM29 mRNA levels are predictive of relapse-free survival in breast cancer patients treated with endocrine therapy. In conclusion, thermal proteome profiling identifies the proteasome and ECM29 protein as mediators of palbociclib activity in breast cancer cells[2].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Palbociclib presents a linear pharmacokinetic profile and its peak plasma concentration was observed 6-12 hours after oral administration. The oral bioavailability is reported to be of 46% with a steady-state reached after 8 days and a median accumulation ratio of 2.4. The absorption of palbociclib is significantly reduced under fasting conditions and hence, food intake is recommended when this drug is administered. The main route of elimination of palbociclib is through feces after hepatic metabolism while renal clearance seems to play a minor role accounting only for 17.5% of the eliminated dose. The mean apparent distribution of palbociclib is 2583 L which suggests that palbociclib penetrates extensively into peripheral tissues. The mean apparent oral clearance of palbociclib is of 63.1 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Palbociclib is mainly hepatically transformed. the metabolism is mainly performed by the activities of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 3A and the sulfotransferase 2A1. The metabolism of palbociclib is represented mainly by reactions of oxidation and sulfonation followed by acylation and glucuronidation as minor reactions. After its metabolism, palbociclib forms mainly inactive glucuronide and sulfamic acid conjugates. The major circulating metabolite, accounting for 1.5% of the dose in excreta is is the glucuronide conjugate. Biological Half-Life The mean plasma elimination half-life of palbociclib is 29 hours. |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity
In the large clinical trials, adverse events were common and led to dose reductions in one-third of patients and discontinuation in 8%. Publications on the efficacy and safety of palbociclib rarely mentioned serum ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity. In a study of women with refractory, metastatic breast cancer, serum ALT elevations occurred in 6% [2% over 5 times ULN] receiving palbociclib and fulvestrant compared to 3% [none over 5 times ULN] on fulvestrant alone. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been several reports of prominent ALT elevations arising after 2 or 3 cycles of palbociclib, that improved on discontinuation and recurred rapidly when restarted. Serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels were normal and symptoms were not mentioned. In addition, there have been rare reports of patients with refractory metastatic breast cancer who developed pseudocirrhosis within 2 to 3 months of starting palbociclib presenting with fatigue, jaundice and ascites with only modest elevations in serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels. Imaging revealed a severely nodular liver, but liver histology showed desmoplastic changes in areas of necrotic metastatic tumor without cirrhosis. The liver also had vascular changes suggestive of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, changes possibly caused by the dramatic involution of the metastatic tumor tissue combined with vascular damage. Pseudocirrhosis has been reported with other highly successful antineoplastic therapies of cancer metastatic to the liver, but the frequency is rare. Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury that may represent pseudocirrhosis from nodular transformation of the liver in response to necrosis of hepatic metastases). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of palbociclib during breastfeeding. Because palbociclib is 85% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 29 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. It is also given in combination with letrozole or fulvestrant, which may increase the risk to the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during palbociclib therapy and for 3 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Binding of palbociclib to human plasma proteins in vitro accounts for approximately 85% of the administered dose. |
||
| References |
[1]. Mol Cancer Ther.2004 Nov;3(11):1427-38;
Cell Death Dis.2018 Apr 18;9(5):446; EMBO J.2018 Apr 18. pii: e98359. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798359. |
||
| Additional Infomation |
Palbociclib is a member of the class of pyridopyrimidines that is 2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino}pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one bearing additional methyl, acetyl and cyclopentyl substituents at positions 5, 6 and 8 respectively. It is used in combination with letrozole for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.22 (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a pyridopyrimidine, an aminopyridine, a secondary amino compound, a member of piperidines, an aromatic ketone, a member of cyclopentanes and a tertiary amino compound.
Palbociclib is a piperazine pyridopyrimidine that acts in the cell cycle machinery. It is a second generation cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor selected from a group of pyridopyrimidine compounds due to its favorable physical and pharmaceutical properties. Palbociclib was developed by Pfizer Inc after the discovery that identified the cyclin-dependent kinases as key regulators of cell growth. It was originally FDA approved on March 2015 for the treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer and its indications were updated in April 2019 to include male patients based on findings from postmarketing reports and electronic health records demonstrating safety and clinical efficacy. Palbociclib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of palbociclib is as a Kinase Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor. Palbociclib is a unique cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that is used in combination with aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer. Palbociclib is associated with transient and usually mild elevations in serum aminotransferase during therapy and to an unusual form of liver injury called pseudocirrhosis caused by shrinkage of tumor metastases in the liver combined with desmoplastic changes and vascular damage, that can be severe, progressive and even fatal. Palbociclib is an orally available cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Palbociclib selectively inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and 6 (CDK6), thereby inhibiting retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation early in the G1 phase leading to cell cycle arrest. This suppresses DNA replication and decreases tumor cell proliferation. CDK4 and 6 are serine/threonine kinases that are upregulated in many tumor cell types and play a key role in the regulation of cell cycle progression. See also: Palbociclib Isethionate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Palbociclib is indicated in combination with [letrozole] as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2)-negative and hormone receptor(HR)-positive tumors in adult patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer. It is as well approved in combination with [fulvestrant] in patients with disease progression with prior endocrine therapy. In the official labeling, the use of palbociclib should be accompanied with either an aromatase inhibition, no restricted to letrozole, as initial endocrine-based therapy in postmenopausal women or in man. The breast cancer starts as a group of cancer cells that grow into and destroy the nearby breast tissue. This growth can spread into other parts of the body which is called metastasis. According to the location of the cancer cells, it can be categorized in ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. However, other types of breast cancer include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast, triple negative breast cancer non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma. In males, breast cancer is usually treated as the cases of postmenopausal women and almost all the cases are ductal carcinoma. FDA Label Ibrance is indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor (HR) positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer : in combination with an aromatase inhibitor; in combination with fulvestrant in women who have received prior endocrine therapy. In pre- or perimenopausal women, the endocrine therapy should be combined with a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist. Treatment of Ewing sarcoma Treatment of breast malignant neoplasms Mechanism of Action Palbociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor that acts by binding to the ATP pocket with an IC50 in the range of 9-15 nmol/L. It is important to consider that it presents low to absent activity against other kinases. The CDK4/6 kinase is involved, with coregulatory partner cyclin D, in the G1-S transition. Hence, inhibition of this step prevents cell cycle progression in cells in whose this pathway is functioning. This step includes the pathways of the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein and the E2F family of transcription factors. Synovial sarcoma is a highly aggressive but rare form of soft tissue malignancy that primarily affects the extremities of the arms or legs, for which current chemotherapeutic agents have not been proven to be very effective. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6-retinoblastoma protein (CDK4/6-Rb) pathway of cell cycle control is known to be aberrant in a large proportion of cancers. Recently, CDK4 inhibitors have successfully been used pre-clinically for the treatment of many human cancers, and in 2015, following the success of clinical trials, the FDA approved the first selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, palbociclib, for the treatment of endocrine therapy resistant breast cancers. However, the expression and therapeutic potential of targeting CDK4 in synovial sarcoma remains unclear. In the present study, we report that CDK4 is highly expressed in human synovial sarcoma, and high CDK4 expressions are associated with poor prognosis in sarcomas patients and the clinical stage and the TNM grade in synovial sarcoma patients. Knockdown of CDK4 with specific small interference RNAs inhibits cell proliferation and enhances apoptotic effects in synovial sarcoma cells. CDK4 inhibitor palbociclib suppresses synovial sarcoma cell proliferation and growth in a dose and time-dependent manner. Palbociclib also inhibits the CDK4/6-Rb signaling pathway and promotes cell apoptosis without changing CDK4/6 protein levels, suggesting that palbociclib only represses the hyper-activation, not the expression of CDK4/6. Flow cytometry analysis reveals that palbociclib induces G1 cell-cycle arrest and apoptotic effects by targeting the CDK4/6-Rb pathway in synovial sarcoma cells. Furthermore, wound healing assays demonstrate that inhibition of the CDK4/6-Rb pathway by palbociclib significantly decreases synovial sarcoma cell migration in vitro. Our study highlights the importance of the CDK4/6-Rb pathway in human synovial sarcoma pathogenesis, and the role of the current selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, palbociclib, as a potential promising targeted therapeutic agent in the treatment of human synovial sarcoma.[1] |
| Exact Mass |
603.2553798
|
|---|---|
| CAS # |
2757498-64-7
|
| Related CAS # |
571190-30-2; 827022-33-3 (isethionate salt); 827022-32-2 (HCl); 1628752-83-9 (Palbociclib D8); 2366269-23-8 (Palbociclib-propargyl) |
| PubChem CID |
164887438
|
| Appearance |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| InChi Key |
HOLXHPZTHUPIFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H29N7O2.C5H4N2O4/c1-15-19-14-27-24(28-20-8-7-18(13-26-20)30-11-9-25-10-12-30)29-22(19)31(17-5-3-4-6-17)23(33)21(15)16(2)32;8-3-1-2(4(9)10)6-5(11)7-3/h7-8,13-14,17,25H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27,28,29);1H,(H,9,10)(H2,6,7,8,11)
|
| Chemical Name |
6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one;2,4-dioxo-1H-pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Palbociclib orotate; Palbociclib (orotate);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples.
Injection Formulations
Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] Oral Formulations
Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). View More
Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
Evaluation of IC50concentrations of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, and their effects on CDK-Rb-E2F signaling in human HPASMCs from healthy donors and IPAH patients.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
Effects of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
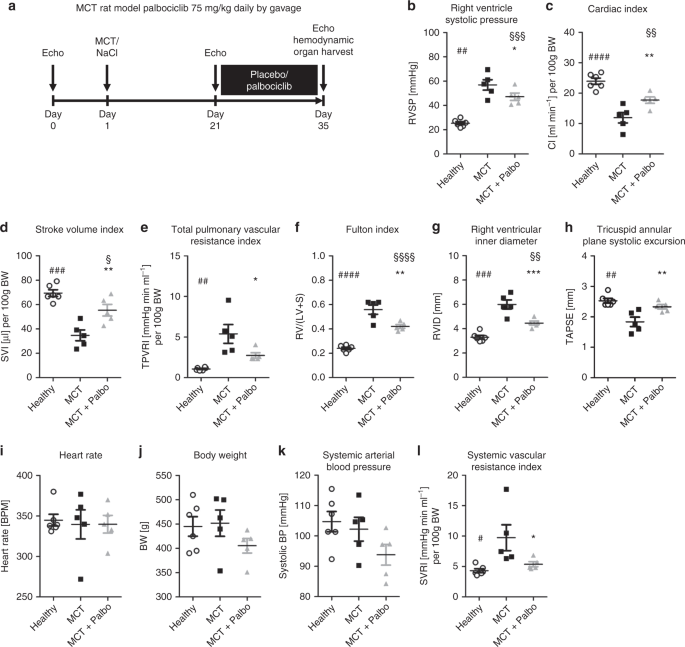 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the MCT rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
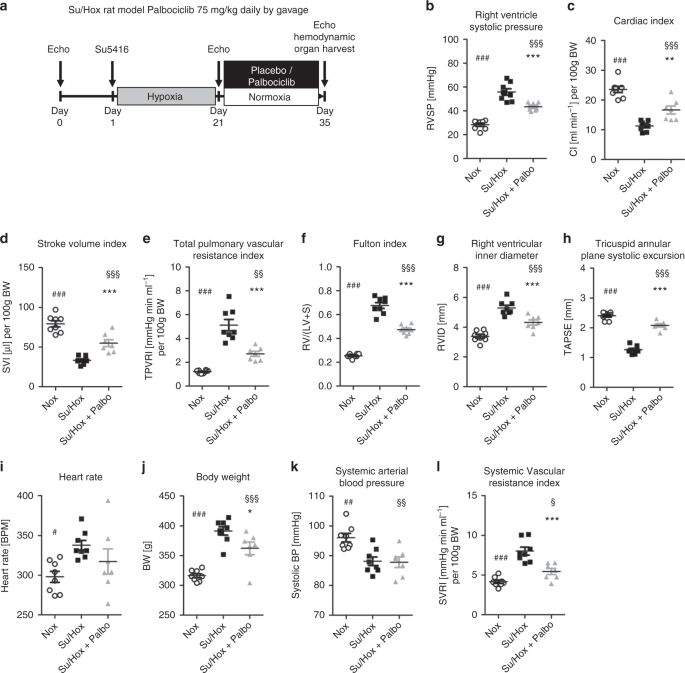 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the Su/Hox rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
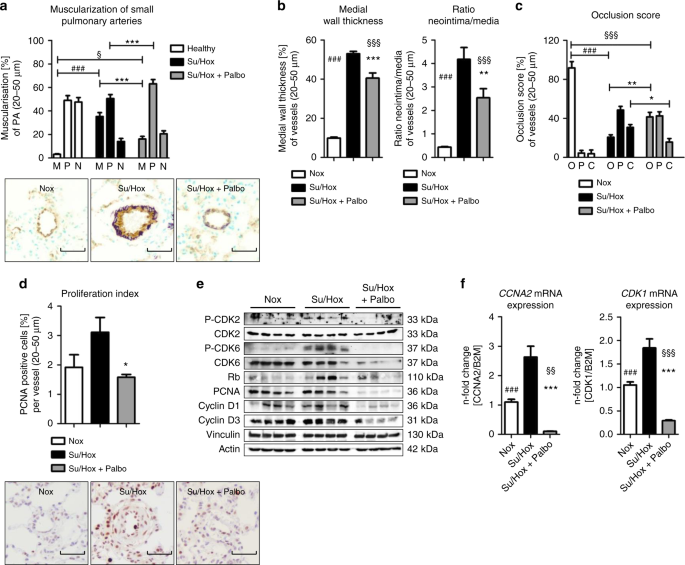 Ex vivo analyses of lung tissue for reversal of remodeling and in vivo drug efficacy in the Su/Hox model.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
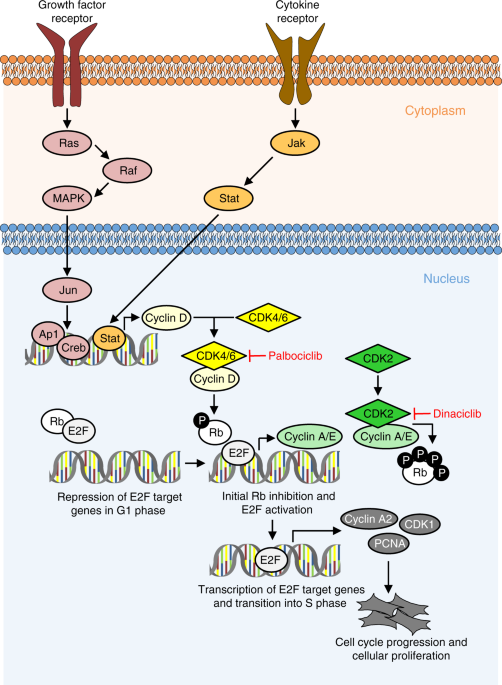 Proposed mechanism of action of palbociclib and dinaciclib in PAH. Multiple growth factors, cytokines, and mitogens induce the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), e.g., by increasing the expression of cyclin D1.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |