
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: =99.05%
Palbociclib HCl (Pfizer trade name Ibrance, also known as PD-0332991), the HCl salt of Palbociclib, is a highly selective, orally bioavailable pyridopyrimidine-derived inhibitor of CDK4/6 with potential antineoplastic activity. In cell-free experiments, it inhibits CDK4 and CDK6 with IC50s of 11 nM and 16 nM, respectively. Many tumor cells overexpress CDK4 and CDK6, and Pfizer's palbociclib is the first CDK4/6 inhibitor to be approved by the FDA as a cancer treatment in 2017. There is no evidence of any activity against PDGFR, EGFR, FGFR, CDK1/2/5, InsR, etc. In vitro, it is a strong anti-proliferative agent that induces an exclusive G1 arrest in Rb-positive tumor cells. It has been shown to cause G1 arrest in primary bone marrow cells and stop tumor growth in disseminated human myeloma xenografts.
| Targets |
DYRK1A (IC50 = 2000 nM); MAPK (IC50 = 8000 nM); Cdk4/cyclin D3 (IC50 = 9 nM); Cdk4/cyclin D1 (IC50 = 11 nM); Cdk6/cyclin D2 (IC50 = 16 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
PD 0332991 has minimal impact on FGFR, PGFR, IR, EGFR, and other protein kinases. PD 0332991 is a Cdk4 non-ATP competitive inhibitor. Because of lowered Rb phosphorylation at Ser780, PD 0332991 inhibits MDA-MB-435 breast carcinoma cells with an IC50 of 66 nM. With IC50 values ranging from 0.04-0.17 μM, PD 0332991 inhibits the thymidine incorporation into the DNA of human leukemias and Rb-positive breast, colon, and lung carcinomas. Rb-negative cells exhibit no activity for PD 0332991. MDA-MB-453 breast and Colo-205 carcinoma cells accumulate cells in G1 in response to PD 0332991. Additionally, PD 0332991 exhibits activity in the immunocompetent model of 5T33MM myeloma cells, making the cells more susceptible to bortezomib-induced cell death.[2] PD 0332991 suppresses MDA-MB-175, ZR-75-30, CAMA-1, MDA-MB-134, HCC-202, and UACC-893, among other luminal ER-positive and HER2-amplified breast cancer cell lines. In these cell lines, PD 0332991 increases the effectiveness of trastuzumab and tamoxifen. In the tamoxifen-resistant MCF7 cells, PD 0332991 increases the sensitivity of tamoxifen.[3] A recent study demonstrates that malignant rhabdoid tumor (MRT) cell lines, such as MP-MRT-AN, KP-MRT-RY, G401, and KP-MRT-NS, can be suppressed by PD 0332991, and that the MRT cell lines' susceptibility to PD 0332991 is inversely connected with p16 expression.[4]
|
| ln Vivo |
PD 0332991 shows total tumor stasis in an MDA-MB-435 xenograft at 150 mg/kg. Additionally, PD 0332991 exhibits broad-spectrum antitumor activity in multiple human tumor xenografts through the down-regulation of genes under the transcriptional control of E2F and the removal of phospho-Rb and the proliferative marker Ki-67 from tumor tissue. [1]
Multiple myeloma (MM) remains incurable partly because no effective cell cycle-based therapy has been available to both control tumor cell proliferation and synergize with cytotoxic killing. PD 0332991 is an orally active small molecule that potently and specifically inhibits Cdk4 and Cdk6. It has been shown to induce rapid G(1) cell cycle arrest in primary human myeloma cells and suppress tumor growth in xenograft models. To improve therapeutic targeting of myeloma progression, we combined tumor suppression by PD 0332991 with cytotoxic killing by bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor widely used in myeloma treatment, in the immunocompetent 5T33MM myeloma model. We show that 5T33MM tumor cells proliferate aggressively in vivo due to expression of cyclin D2, elevation of Cdk4, and impaired p27(Kip1) expression, despite inhibition of Cdk4/6 by p18(INK4c) and the maintenance of a normal plasma cell transcription program. PD 0332991 potently inhibits Cdk4/6-specific phosphorylation of Rb and cell cycle progression through G(1) in aggressively proliferating primary 5T33MM cells, in vivo and ex vivo. This leads to tumor suppression and a significant improvement in survival. Moreover, induction of G(1) arrest by PD 0332991 sensitizes 5T33MM tumor cells to killing by bortezomib. Inhibition of Cdk4/6 by PD 0332991, therefore, effectively controls myeloma tumor expansion and sensitizes tumor cells to bortezomib killing in the presence of an intact immune system, thereby representing a novel and promising cell cycle-based combination therapy.[2] |
| Enzyme Assay |
CDK assays are run in 96-well filter plates for kinetic analysis and IC50 calculations. By infecting insect cells with baculovirus, all CDK-cyclin kinase complexes are expressed and purified. A portion of pRb fused to GST (amino acids 792–928) serves as the substrate for the assays (GST•RB-Cterm). 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 10 mM MgCl2, 25 μM ATP (for CDK4-cyclin D1, CDK6-cyclin D2, and CDK6-cyclin D3), 0.25 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP, 20 ng of enzyme, 1 μg of GST•RB-Cterm, and suitable dilutions of inhibitor are included in the overall reaction volume of 0.1 mL. After adding all the ingredients to the wells—aside from the [γ-32P]ATP—they are put on a plate mixer for two minutes. Addition of [γ-32P]ATP initiates the reaction, which is then incubated for 15 minutes at 25°C. In order to allow the substrate to precipitate, the reaction is stopped by adding 0.1 mL of 20% trichloroacetic acid and keeping the plate at 4°C for at least an hour. After five well washes with 0.2 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid, radioactive incorporation is measured using a β plate counter.
|
| Cell Assay |
In a 96-well plate, 2 × 104 cells are seeded per well and incubated for a full night. After being added to the wells, PD 0332991 (0.01-1 μM) is incubated for an additional 24 hours at 37 °C. [14C]Thymidine (0.1 μCi) is added to each well and incorporation of the radiolabel is allowed to proceed for 72 hours. Using a β plate counter, one can determine the incorporerated radioactivity.
Forty-seven human breast cancer and immortalized cell lines representing the known molecular subgroups of breast cancer were treated with PD 0332991 to determine IC50 values. These data were analyzed against baseline gene expression data to identify genes associated with PD 0332991 response. Results: Cell lines representing luminal estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) subtype (including those that are HER2 amplified) were most sensitive to growth inhibition by PD 0332991 while nonluminal/basal subtypes were most resistant. Analysis of variance identified 450 differentially expressed genes between sensitive and resistant cells. pRb and cyclin D1 were elevated and CDKN2A (p16) was decreased in the most sensitive lines. Cell cycle analysis showed G0/G1 arrest in sensitive cell lines and Western blot analysis demonstrated that Rb phosphorylation is blocked in sensitive lines but not resistant lines. PD 0332991 was synergistic with tamoxifen and trastuzumab in ER+ and HER2-amplified cell lines, respectively. PD 0332991 enhanced sensitivity to tamoxifen in cell lines with conditioned resistance to ER blockade. Conclusions: These studies suggest a role for CDK4/6 inhibition in some breast cancers and identify criteria for patient selection in clinical studies of PD 0332991[3]. Malignant rhabdoid tumor (MRT) is a rare and highly aggressive neoplasm of young children. MRT is characterized by inactivation of integrase interactor 1 (INI1). Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), which acts downstream of INI1, is required for the proliferation of MRT cells. Here we investigated the effects of PD 0332991 (PD), a potent inhibitor of CDK4, against five human MRT cell lines (MP-MRT-AN, KP-MRT-RY, G401, KP-MRT-NS, KP-MRT-YM). In all of the cell lines except KP-MRT-YM, PD inhibited cell proliferation >50%, (IC(50) values 0.01 to 0.6 μM) by WST-8 assay, and induced G1-phase cell cycle arrest, as shown by flow cytometry and BrdU incorporation assay. The sensitivity of the MRT cell lines to PD was inversely correlated with p16 expression (r=0.951). KP-MRT-YM cells overexpress p16 and were resistant to the growth inhibitory effect of PD. Small interfering RNA against p16 significantly increased the sensitivity of KP-MRT-YM cells to PD (p<0.05). These results suggest that p16 expression in MRT could be used to predict its sensitivity to PD. PD may be an attractive agent for patients with MRT whose tumors express low levels of p16 [4]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Advanced stage human tumor xenografts including Colo-205, MDA-MB-435 breast, SF-295 glioblastoma, ZR-75-1 breast, PC-3 prostate, H125 lung, SW-620 colon, H23 lung and MDA-MB-468 breast (Rb negative) are established in severe combined immunodeficient mice.
0-150 mg/kg Given by gavage Multiple myeloma (MM) remains incurable partly because no effective cell cycle-based therapy has been available to both control tumor cell proliferation and synergize with cytotoxic killing. PD 0332991 is an orally active small molecule that potently and specifically inhibits Cdk4 and Cdk6. It has been shown to induce rapid G(1) cell cycle arrest in primary human myeloma cells and suppress tumor growth in xenograft models. To improve therapeutic targeting of myeloma progression, we combined tumor suppression by PD 0332991 with cytotoxic killing by bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor widely used in myeloma treatment, in the immunocompetent 5T33MM myeloma model. We show that 5T33MM tumor cells proliferate aggressively in vivo due to expression of cyclin D2, elevation of Cdk4, and impaired p27(Kip1) expression, despite inhibition of Cdk4/6 by p18(INK4c) and the maintenance of a normal plasma cell transcription program. PD 0332991 potently inhibits Cdk4/6-specific phosphorylation of Rb and cell cycle progression through G(1) in aggressively proliferating primary 5T33MM cells, in vivo and ex vivo. This leads to tumor suppression and a significant improvement in survival. Moreover, induction of G(1) arrest by PD 0332991 sensitizes 5T33MM tumor cells to killing by bortezomib. Inhibition of Cdk4/6 by PD 0332991, therefore, effectively controls myeloma tumor expansion and sensitizes tumor cells to bortezomib killing in the presence of an intact immune system, thereby representing a novel and promising cell cycle-based combination therapy.[2] |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Palbociclib presents a linear pharmacokinetic profile and its peak plasma concentration was observed 6-12 hours after oral administration. The oral bioavailability is reported to be of 46% with a steady-state reached after 8 days and a median accumulation ratio of 2.4. The absorption of palbociclib is significantly reduced under fasting conditions and hence, food intake is recommended when this drug is administered. The main route of elimination of palbociclib is through feces after hepatic metabolism while renal clearance seems to play a minor role accounting only for 17.5% of the eliminated dose. The mean apparent distribution of palbociclib is 2583 L which suggests that palbociclib penetrates extensively into peripheral tissues. The mean apparent oral clearance of palbociclib is of 63.1 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Palbociclib is mainly hepatically transformed. the metabolism is mainly performed by the activities of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 3A and the sulfotransferase 2A1. The metabolism of palbociclib is represented mainly by reactions of oxidation and sulfonation followed by acylation and glucuronidation as minor reactions. After its metabolism, palbociclib forms mainly inactive glucuronide and sulfamic acid conjugates. The major circulating metabolite, accounting for 1.5% of the dose in excreta is is the glucuronide conjugate. Biological Half-Life The mean plasma elimination half-life of palbociclib is 29 hours. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity
In the large clinical trials, adverse events were common and led to dose reductions in one-third of patients and discontinuation in 8%. Publications on the efficacy and safety of palbociclib rarely mentioned serum ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity. In a study of women with refractory, metastatic breast cancer, serum ALT elevations occurred in 6% [2% over 5 times ULN] receiving palbociclib and fulvestrant compared to 3% [none over 5 times ULN] on fulvestrant alone. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been several reports of prominent ALT elevations arising after 2 or 3 cycles of palbociclib, that improved on discontinuation and recurred rapidly when restarted. Serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels were normal and symptoms were not mentioned. In addition, there have been rare reports of patients with refractory metastatic breast cancer who developed pseudocirrhosis within 2 to 3 months of starting palbociclib presenting with fatigue, jaundice and ascites with only modest elevations in serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels. Imaging revealed a severely nodular liver, but liver histology showed desmoplastic changes in areas of necrotic metastatic tumor without cirrhosis. The liver also had vascular changes suggestive of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, changes possibly caused by the dramatic involution of the metastatic tumor tissue combined with vascular damage. Pseudocirrhosis has been reported with other highly successful antineoplastic therapies of cancer metastatic to the liver, but the frequency is rare. Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury that may represent pseudocirrhosis from nodular transformation of the liver in response to necrosis of hepatic metastases). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of palbociclib during breastfeeding. Because palbociclib is 85% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 29 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. It is also given in combination with letrozole or fulvestrant, which may increase the risk to the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during palbociclib therapy and for 3 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Binding of palbociclib to human plasma proteins in vitro accounts for approximately 85% of the administered dose. |
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Malignant rhabdoid tumor (MRT) is a rare and highly aggressive neoplasm of young children. MRT is characterized by inactivation of integrase interactor 1 (INI1). Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), which acts downstream of INI1, is required for the proliferation of MRT cells. Here we investigated the effects of PD 0332991 (PD), a potent inhibitor of CDK4, against five human MRT cell lines (MP-MRT-AN, KP-MRT-RY, G401, KP-MRT-NS, KP-MRT-YM). In all of the cell lines except KP-MRT-YM, PD inhibited cell proliferation >50%, (IC(50) values 0.01 to 0.6 μM) by WST-8 assay, and induced G1-phase cell cycle arrest, as shown by flow cytometry and BrdU incorporation assay. The sensitivity of the MRT cell lines to PD was inversely correlated with p16 expression (r=0.951). KP-MRT-YM cells overexpress p16 and were resistant to the growth inhibitory effect of PD. Small interfering RNA against p16 significantly increased the sensitivity of KP-MRT-YM cells to PD (p<0.05). These results suggest that p16 expression in MRT could be used to predict its sensitivity to PD. PD may be an attractive agent for patients with MRT whose tumors express low levels of p16.[4]
Cell lines representing luminal estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) subtype (including those that are HER2 amplified) were most sensitive to growth inhibition by PD 0332991 while nonluminal/basal subtypes were most resistant. Analysis of variance identified 450 differentially expressed genes between sensitive and resistant cells. pRb and cyclin D1 were elevated and CDKN2A (p16) was decreased in the most sensitive lines. Cell cycle analysis showed G0/G1 arrest in sensitive cell lines and Western blot analysis demonstrated that Rb phosphorylation is blocked in sensitive lines but not resistant lines. PD 0332991 was synergistic with tamoxifen and trastuzumab in ER+ and HER2-amplified cell lines, respectively. PD 0332991 enhanced sensitivity to tamoxifen in cell lines with conditioned resistance to ER blockade.[3] Palbociclib is a member of the class of pyridopyrimidines that is 2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino}pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one bearing additional methyl, acetyl and cyclopentyl substituents at positions 5, 6 and 8 respectively. It is used in combination with letrozole for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.22 (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a pyridopyrimidine, an aminopyridine, a secondary amino compound, a member of piperidines, an aromatic ketone, a member of cyclopentanes and a tertiary amino compound. Palbociclib is a piperazine pyridopyrimidine that acts in the cell cycle machinery. It is a second generation cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor selected from a group of pyridopyrimidine compounds due to its favorable physical and pharmaceutical properties. Palbociclib was developed by Pfizer Inc after the discovery that identified the cyclin-dependent kinases as key regulators of cell growth. It was originally FDA approved on March 2015 for the treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer and its indications were updated in April 2019 to include male patients based on findings from postmarketing reports and electronic health records demonstrating safety and clinical efficacy. Palbociclib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of palbociclib is as a Kinase Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor. Palbociclib is a unique cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that is used in combination with aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer. Palbociclib is associated with transient and usually mild elevations in serum aminotransferase during therapy and to an unusual form of liver injury called pseudocirrhosis caused by shrinkage of tumor metastases in the liver combined with desmoplastic changes and vascular damage, that can be severe, progressive and even fatal. Palbociclib is an orally available cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Palbociclib selectively inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and 6 (CDK6), thereby inhibiting retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation early in the G1 phase leading to cell cycle arrest. This suppresses DNA replication and decreases tumor cell proliferation. CDK4 and 6 are serine/threonine kinases that are upregulated in many tumor cell types and play a key role in the regulation of cell cycle progression. See also: Palbociclib Isethionate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Palbociclib is indicated in combination with [letrozole] as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2)-negative and hormone receptor(HR)-positive tumors in adult patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer. It is as well approved in combination with [fulvestrant] in patients with disease progression with prior endocrine therapy. In the official labeling, the use of palbociclib should be accompanied with either an aromatase inhibition, no restricted to letrozole, as initial endocrine-based therapy in postmenopausal women or in man. The breast cancer starts as a group of cancer cells that grow into and destroy the nearby breast tissue. This growth can spread into other parts of the body which is called metastasis. According to the location of the cancer cells, it can be categorized in ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. However, other types of breast cancer include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast, triple negative breast cancer non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma. In males, breast cancer is usually treated as the cases of postmenopausal women and almost all the cases are ductal carcinoma. FDA Label Ibrance is indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor (HR) positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer : in combination with an aromatase inhibitor; in combination with fulvestrant in women who have received prior endocrine therapy. In pre- or perimenopausal women, the endocrine therapy should be combined with a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist. Treatment of Ewing sarcoma Treatment of breast malignant neoplasms Mechanism of Action Palbociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor that acts by binding to the ATP pocket with an IC50 in the range of 9-15 nmol/L. It is important to consider that it presents low to absent activity against other kinases. The CDK4/6 kinase is involved, with coregulatory partner cyclin D, in the G1-S transition. Hence, inhibition of this step prevents cell cycle progression in cells in whose this pathway is functioning. This step includes the pathways of the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein and the E2F family of transcription factors. |
| Molecular Formula |
C24H29N7O2.HCL
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
483.99
|
| Exact Mass |
483.214
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 59.56; H, 6.25; Cl, 7.33; N, 20.26; O, 6.61
|
| CAS # |
827022-32-2
|
| Related CAS # |
Palbociclib;571190-30-2;Palbociclib hydrochloride;571189-11-2;Palbociclib-d8;1628752-83-9;Palbociclib isethionate;827022-33-3;Palbociclib dihydrochloride;Palbociclib orotate;2757498-64-7
|
| PubChem CID |
11431660
|
| Appearance |
Yellow solid powder
|
| Boiling Point |
727ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| Flash Point |
393.5ºC
|
| LogP |
4.234
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
8
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
5
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
34
|
| Complexity |
775
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
Cl.O=C1N(C2CCCC2)C2C(=CN=C(NC3C=CC(N4CCNCC4)=CN=3)N=2)C(C)=C1C(C)=O
|
| InChi Key |
STEQOHNDWONVIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H29N7O2.ClH/c1-15-19-14-27-24(28-20-8-7-18(13-26-20)30-11-9-25-10-12-30)29-22(19)31(17-5-3-4-6-17)23(33)21(15)16(2)32;/h7-8,13-14,17,25H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27,28,29);1H
|
| Chemical Name |
6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one;hydrochloride
|
| Synonyms |
Palbociclib; PD-332991; PD332991; PD 332991; PD0332991; PD-0332991; PD0332991 HCl, PD-0332991 hydrochloride; Palbociclib HCl; Palbociclib (hydrochloride); PD 0332991 HCl; Palbociclib (PD-0332991) HCl; PD-0332991 hydrochloride; BKC4F3Q5XL; PD 0332991; Palbociclib HCl; Trade name: Ibrance
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.54 mg/mL (1.12 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 5.4 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.54 mg/mL (1.12 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 5.4 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: Saline: 20 mg/mL Solubility in Formulation 4: 20 mg/mL (41.32 mM) in 0.5%HPMC 1%Tween80 (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. Solubility in Formulation 5: 4.17 mg/mL (8.62 mM) in Lactic acid buffer (50 mM, pH 4.0) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0662 mL | 10.3308 mL | 20.6616 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4132 mL | 2.0662 mL | 4.1323 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2066 mL | 1.0331 mL | 2.0662 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06003114 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib | Breast Cancer | Pfizer | September 2015 | |
| NCT03936270 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib 125mg Drug: Letrozole 2.5mg |
Ovarian Cancer | Latin American Cooperative Oncology Group |
January 27, 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02738866 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib Drug: Fulvestrant |
Metastatic Breast Cancer | Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins |
October 25, 2016 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05069038 | Recruiting | Drug: Palbociclib 125mg | Breast Cancer | University of Nebraska | March 2, 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04360941 | Recruiting | Drug: Palbociclib Drug: Avelumab |
ER+ Breast Cancer Recurrent Breast Cancer |
Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust |
August 11, 2020 | Phase 1 |
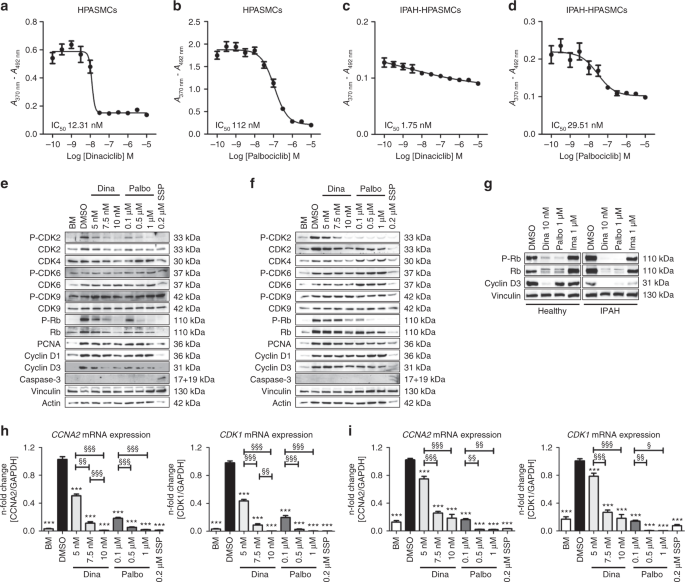 Evaluation of IC50concentrations of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, and their effects on CDK-Rb-E2F signaling in human HPASMCs from healthy donors and IPAH patients.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
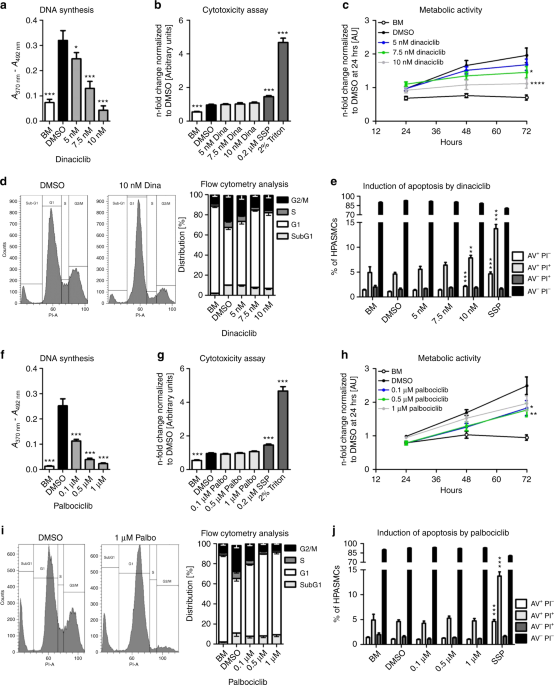 Effects of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
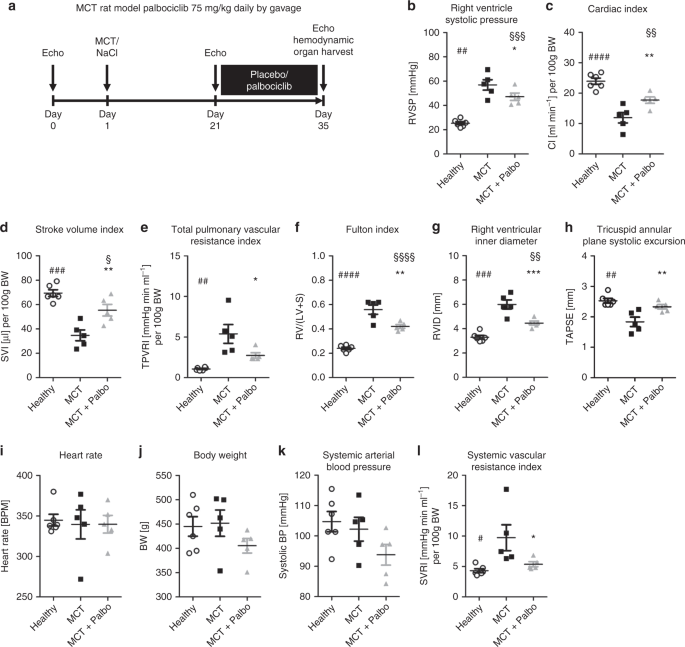 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the MCT rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
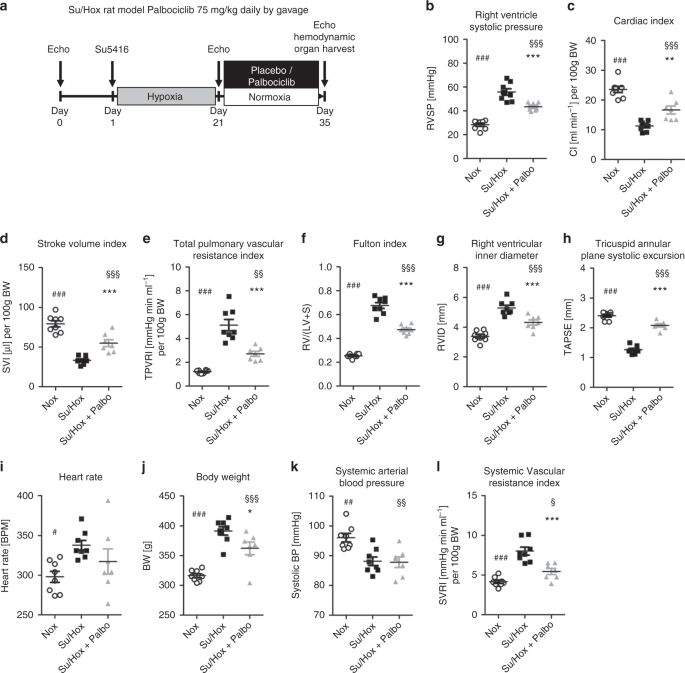 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the Su/Hox rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
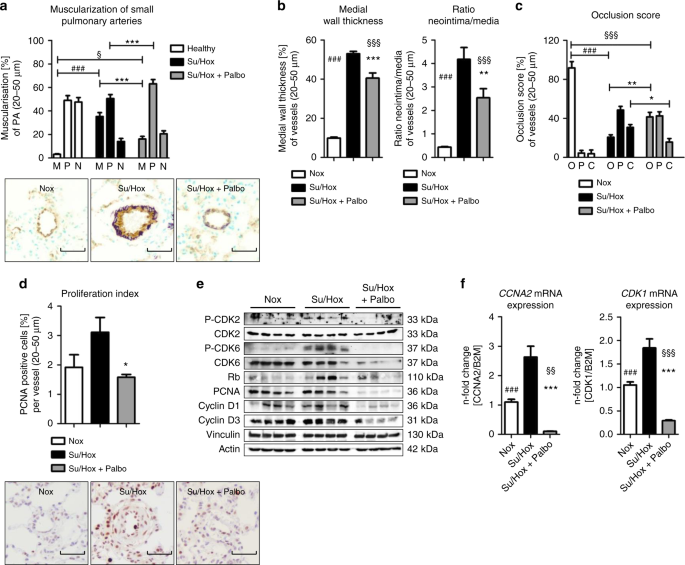 Ex vivo analyses of lung tissue for reversal of remodeling and in vivo drug efficacy in the Su/Hox model.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
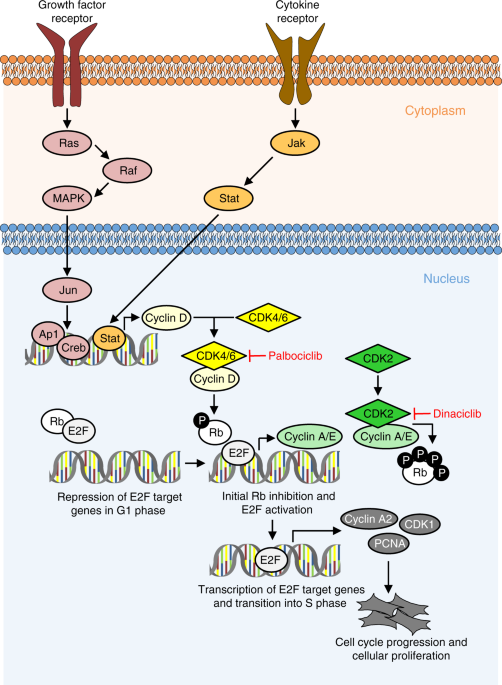 Proposed mechanism of action of palbociclib and dinaciclib in PAH. Multiple growth factors, cytokines, and mitogens induce the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), e.g., by increasing the expression of cyclin D1.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|
|---|
|
|