
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Pancuronium dibromide (OrgNA97; NA-97; Org NA 97; Pavulon), a neuromuscular relaxant used in euthanasia, is a bis-quaternary steroid and a competitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 5.5 nM. As a neuromuscular blocking agent, Pancuronium bromide is more potent than curare but has less effect on the circulatory system and on histamine release. Pancuronium dibromide interrupts neuromuscular transmission by competing with acetylcholine for receptor sites on the motor end-plate.
| ln Vitro |
Pancuronium's effect on transmembrane sodium conductance is examined in chick embryonic dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pancuronium, when externally perfused at concentrations between 50 μM and 1 mM, quickly and reversibly inhibits current flow. With a half-effective dose of 170 μM, inhibition is concentration-dependent but not voltage-dependent. By interacting with the sodium channels in both the resting and open states, pancuronium may lower the sodium current[2].
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vivo |
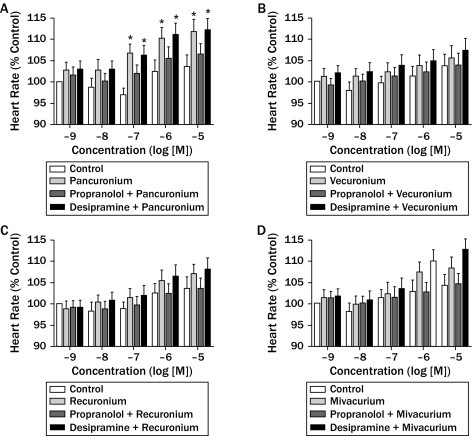
In male guinea pigs weighing 250–300 g, pancuronium (0.5 mg/kg) administered intravenously reverses the bradycardia caused by vagal nerve stimulation and injected acetylcholine (ACh). Vagally-induced bronchoconstriction is amplified by pancuronium (0.04 mg/kg) at levels that result in 100% neuromuscular blockade[1]. Rat anococcygeus and vas deferens exhibit pancuronium-mediated adrenergic nerve stimulation potentiation[3].
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. A D Fryer, et al. Pancuronium and gallamine are antagonists for pre- and post-junctional muscarinic receptors in the guinea-pig lung. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;335(4):367-71.
[2]. E Maestrone, et al. Extracellular pancuronium affects sodium current in chick embryo sensory neurons. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):283-7. [3]. J R Docherty, et al. A comparison of the effects of pancuronium bromide and its monoquaternary analogue, ORG NC 45, on autonomic and somatic neurotransmission in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(1):225-33. |
| Molecular Formula |
C35H60N2O4.2BR
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
732.67
|
|
| CAS # |
15500-66-0
|
|
| Related CAS # |
16974-53-1 (cation);15500-66-0 (bromide);22189-36-2 (bromide hydrate);
|
|
| Appearance |
Typically exists as solids (or liquids in special cases) at room temperature
|
|
| SMILES |
[Br-].[Br-].O(C(C([H])([H])[H])=O)[C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@]2([H])[C@]1(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]1([H])[C@@]3(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@]3([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]21[H])OC(C([H])([H])[H])=O)[N+]1(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])[N+]1(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
NPIJXCQZLFKBMV-YTGGZNJNSA-L
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C35H60N2O4.2BrH/c1-24(38)40-32-21-26-13-14-27-28(35(26,4)23-31(32)37(6)19-11-8-12-20-37)15-16-34(3)29(27)22-30(33(34)41-25(2)39)36(5)17-9-7-10-18-36;;/h26-33H,7-23H2,1-6H3;2*1H/q+2;;/p-2/t26-,27+,28-,29-,30-,31-,32-,33-,34-,35-;;/m0../s1
|
|
| Chemical Name |
1,1-((2S,3S,5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,16S,17R)-3,17-diacetoxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-2,16-diyl)bis(1-methylpiperidin-1-ium) bromide
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 100 mg/mL (136.49 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3649 mL | 6.8244 mL | 13.6487 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2730 mL | 1.3649 mL | 2.7297 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1365 mL | 0.6824 mL | 1.3649 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
 |
|---|
|