
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Rigosertib (formerly also known as ON-01910) is a novel, potent and non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of PLK1 with IC50 of 9 nM in a cell-free assay. It exhibits no activity toward Plk3 and a 30-fold increase in selectivity against Plk2. It may be possible to treat cancer with rigosertib. Polo-like kinase1 (Plk1) is inhibited by rigosertib, which causes reversible cell arrest at the G1 and G2 stage without apoptosis in normal cells and selective G2/M arrest followed by apoptosis in a variety of tumor cells. When used in conjunction with other chemotherapeutic agents, this agent may show synergistic antitumor activity.
| Targets |
PLK1 (IC50 = 9 nM); PLK2 (IC50 = 260 nM); PDGFR (IC50 = 18 nM); Src (IC50 = 155 nM); BCR-ABL (IC50 = 32 nM); Cdk1 (IC50 = 260 nM); Flt1 (IC50 = 42 nM); Fyn (IC50 = 182 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
Rigosertib, which has an IC50 of 9 nM, is a non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of PLK1. Moreover, rigosertib shows inhibition with an IC50 of 18-260 nM against PLK2, PDGFR, Flt1, BCR-ABL, Fyn, Src, and CDK1. 94 distinct tumor cell lines, including BT27, MCF-7, DU145, PC3, U87, A549, H187, RF1, HCT15, SW480, and KB cells, exhibit cell killing activity in response to rigosertib, with an IC50 of 50–250 nM. Rigosertib, however, has little to no effect in normal cells, such as HFL, PrEC, HMEC, and HUVEC, unless the concentration is higher than 5–10 μM. Rigosertib (100-250 nM) causes spindle abnormalities and apoptosis in HeLa cells.[1] With an IC50 of 50-100 nM, rigorsertib also inhibits a number of multidrug-resistant tumor cell lines, such as MES-SA, MES-SA/DX5a, CEM, and CEM/C2a. Rigosertib (0.25–5 μM) causes an accumulation of cells with subG1 DNA content, initiates apoptotic pathways, and inhibits cell cycle progression in G2/M phase in DU145 cells. Rigosertib (50 nM-0.5 μM) causes caspase 3/7 activation and viability loss in A549 cells.[2] According to a recent study, rigosertib causes CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) cells to undergo apoptosis without harming healthy B-cells or T-cells. Additionally, rigorsertib inhibits the migration of leukemic cells induced by SDF-1 and nullifies the pro-survival effect of follicular dendritic cells on CLL cells.[3]
|
| ln Vivo |
Rigosertib (250 mg/kg) significantly inhibits tumor growth in mouse xenograft models of MCF-7, MIA-PaCa, and Bel-7402 cells.[1] A mouse xengraft model of BT20 cells demonstrates the inhibitory effect of rigosertib (200 mg/kg) on tumor growth.[2]
In order to determine in vivo efficacy, we utilized the nude mouse model system. A highly aggressive human estrogen negative breast carcinoma cell line (BT20) was xenografted into athymic nude mice. The animals were treated with 200 mg/kg of 28 (Rigosertib) using a Q2D × 20 schedules. The animals were treated when the tumors were approximately 70 mm3 in size. Figure 5A shows that an intraperitonial (IP) injection of Rigosertib was able to significantly inhibit the growth of the tumors. The tumors of vehicle treated mice, on average, increased in volume over the 22 day period by 5 fold (70 mm3–480 mm3), while the Q2D Rigosertib treated tumors increased in volume by only 2.5 fold (70 mm3–180 mm3). Rigosertib were well tolerated at these doses as determined by body weights and physical observations (Figure 5B). These studies show that Rigosertib is efficacious against human tumor xenografts while showing no signs of toxicity at the schedules tested under this study.[1] In vivo, Rigosertib did not exhibit hematotoxicity, liver damage, or neurotoxicity, and was a potent inhibitor of tumor growth in a variety of xenograft nude mouse models. Rigosertib /ON01910 showed strong synergy with several chemotherapeutic agents, often inducing complete regression of tumors[1]. |
| Enzyme Assay |
For 30 minutes at room temperature, recombinant PLK1 (10 ng) is incubated with varying concentrations of rigosertib in a 15 µL reaction mixture (50 mM HEPES, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 2 mM Dithiothreitol, 0.01% NP-40 [pH 7.5]). 20 µL (15 µL enzyme + inhibitor, 2 µL 1 mM ATP), 2 µL of γ32P-ATP (40 μCi), and 1 µL of recombinant Cdc25C (100 ng) or casein (1 μg) substrates are used in kinase reactions, which are carried out for 20 min at 30 °C. Boiling in 20 µL of 2× Laemmli buffer for 2 minutes ends the reaction. 18% SDS-PAGE is used to separate phosphorylated substrates. After drying, the gels are exposed to X-ray film for three to ten minutes.
|
| Cell Assay |
Cytotoxicity of Rigosertib (ON 01910.Na) against CLL cells from 34 patients was determined in vitro with flow cytometry of cells stained with Annexin V and CD19. Global gene expression profiling on Affymetrix microarrays, flow cytometry, Western blotting, and cocultures with stroma cells were used to delineate ON 01910.Na mechanism of action.[3]
Cytotoxicity Assay[2] Researchers tested a number of tumor cell lines using a dose response end point assay system. The cells were grown in either DMEM or RPMI supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1unit/mL Penicillin-Streptomycin solution. The tumor cells were plated into 6 well dishes at a cell density of 1.0 × 105 cells/mL/well and compounds were added 24 h later at various concentrations. Cell counts were determined from duplicate wells after 96 h of treatment. The total number of viable cells was determined by trypan blue exclusion. Flow Cytometry Human prostate tumor cells, DU145 cells, and normal diploid human lung fibroblasts, HFL-1 cells, were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1 unit/mL penicillin-streptomycin. The cells were plated onto 100 mm2 dishes at a cell density of 1.0 × 106 cells/dish, and 24 h later, they were treated with 2.5 μM of the compound. The cells were harvested 24 h after treatment. The cells were removed from the plate by trypsin digestion and combined with the non-attached cells found in the medium. The cell pellets were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and fixed in ice cold 70% ethanol for at least 24 h. The fixed cells were then washed with room temperature PBS and stained with propidium iodide (50 mg/mL) and RNase A (0.5 mg) for 30 min at 37 °C. The stained cells were then analyzed on a Becton-Dickinson flow cytometer and the data analyzed by cell cycle analysis software. PARP Western [2] DU145 and HFL-1 cells were plated at a density of 3.0 × 106 cells per 150 mm2 plate and treated 24 h later with either DMSO or 28. The cells were collected 48 h treatment and cell pellets were frozen. The frozen cell pellets were lysed in 1% NP40/PBS lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors. Equal amounts of total cellular protein was then resolved on a 10%-SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The gels were transferred onto nitrocellulose paper (S/S), hybridized with anti-PARP antibodies (BD) and developed using ECL solution. Cellular Viability and Caspase 3/7 Activity [2] Exponentially growing A549 cells were seeded in a white walled 96-well plate at a density of 3,600 cells/well in 100 μl of DMEM containing 10% FBS and 1% Pen/Strep. Cells were then allowed to adhere overnight at 37 °C in an incubator. The next day, cells were treated with varying concentrations of 28 or DMSO and then returned to the incubator. 24 h later, plates were removed from the incubator and 20 μL of CellTiter-Blue® Reagent was added individually to each well following manufacturer’s instructions. Plates were slowly shaken for 0.5 min and then returned to the incubator. After 3 h, fluorescence was read using a Glomax 96-well plate reader. Next, 120 μL of Caspase Glo® 3/7 Reagent was added to each well per manufacturer’s instructions. Plates were slowly shaken for 0.5 min and allowed to develop at room temperature for 2 h. At the end of this period, luminescence was read using a Glomax 96-well plate reader. One day later, different concentrations of Rigosertib are added to six-well dishes containing 1×105 cells/mL/well of tumor cells that have been plated. After treatment for 96 hours, cell counts are obtained from duplicate wells. By using trypan blue exclusion, the total number of viable cells is found. |
| Animal Protocol |
Bel-7402 tumor models: subcutaneous injection of 1 × 107 Bel-7402 tumor cells is given to twenty female athymic (NCR-nu/nu) nude mice. Ten to fourteen days later, when the tumor volumes reach 200–250 mm, the mice are divided into four groups, each of which has tumors of the same volume. Alternatively, NSC 266046 (100 mg/kg) and rigosertib (ON01910, 250 mg/kg) can be given intraperitonially on different days. Using traceable digital vernier calipers, tumor measurements are performed twice a week. During every measurement, body weight is calculated. Signs of toxicity in the animals are monitored.
Nude mouse assay [2] Female athymic (NCR-nu/nu, Taconic) nude mice were injected with 0.5–1.0 x107 BT20 cells subcutaneously in the hind leg using a 1 mL tuberculin syringe equipped with a 271/2 gauge needle. Approximately 14 days later, mice were paired (N=9) and injected with 200 mg/Kg 28 or Phosphate buffered saline as the vehicle control. The intravenous injections were performed in the mouse tail vein using a 1 mL tuberculin syringe equipped with a 30 gauge needle. The animals were injected following a Q2D X 20 schedule. Tumor measurements (two dimensions) were done three times per week using traceable digital vernier calipers. Tumor volume was calculated using the following equation: V= (Lx(S2)p/6, where L is the longer and S is the shorter of the two dimensions. Body weight was determined during each measurement. The animals were observed for signs of toxicity. The time of tumor volume doubling was calculated and the T-C value (difference in the average times post treatment for tumors of the treated groups to attain a doubling in volume compared to the average of the control group) was determined. We did not observe body weight loss of more than 10% in any group nor were there any animal deaths. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
In vivo, this compound did not exhibit hematotoxicity, liver damage, or neurotoxicity, and was a potent inhibitor of tumor growth in a variety of xenograft nude mouse models. ON01910 showed strong synergy with several chemotherapeutic agents, often inducing complete regression of tumors.
|
| References | |
| Additional Infomation |
Rigosertib is an N-[2-methoxy-5-({[2-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]sulfonyl}methyl)phenyl]glycine in which the double bond has E-configuration. It is a non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of PLK1 with an IC50 of 9 nM and exhibits anti-cancer properties. It has a role as a microtubule-destabilising agent, an EC 2.7.11.21 (polo kinase) inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer and an antineoplastic agent. It is a conjugate acid of a rigosertib(1-).
Rigosertib has been used in trials studying the treatment and basic science of MDS, RAEB, Cancer, Hepatoma, and Neoplasms, among others. Rigosertib is a synthetic benzyl styryl sulfone analogue and Ras mimetic, with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, rigosertib targets and binds to Ras-binding domain (RBD) found in many Ras effector proteins, including Raf kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). This prevents Ras from binding to its targets and inhibits Ras-mediated signaling pathways, including Ras/Raf/Erk, Ras/CRAF/polo-like kinase1 (Plk1), and Ras/ PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. This induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in a variety of susceptible tumor cells. |
| Molecular Formula |
C21H25NO8S
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
451.4901
|
| Exact Mass |
451.13
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 55.87; H, 5.58; N, 3.10; O, 28.35; S, 7.10
|
| CAS # |
592542-59-1
|
| Related CAS # |
Rigosertib sodium;592542-60-4;(E/Z)-Rigosertib sodium;1225497-78-8
|
| PubChem CID |
6918736
|
| Appearance |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| Density |
1.332±0.06 g/cm3
|
| Melting Point |
172-174 ºC (acetone )
|
| LogP |
3.957
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
9
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
11
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
31
|
| Complexity |
678
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=S(/C=C/C(C(OC)=C1)=C(OC)C=C1OC)(CC2=CC=C(OC)C(NCC(O)=O)=C2)=O
|
| InChi Key |
OWBFCJROIKNMGD-BQYQJAHWSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H25NO8S/c1-27-15-10-19(29-3)16(20(11-15)30-4)7-8-31(25,26)13-14-5-6-18(28-2)17(9-14)22-12-21(23)24/h5-11,22H,12-13H2,1-4H3,(H,23,24)/b8-7+
|
| Chemical Name |
2-[2-methoxy-5-[[(E)-2-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]sulfonylmethyl]anilino]acetic acid
|
| Synonyms |
ON-01910; ON01910; ON 01910; Rigosertib; 592542-59-1; UNII-67DOW7F9GL; ON-01910; Rigosertib [USAN:INN]; 67DOW7F9GL; Rigosertib [USAN];brand name: Estybon
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. (2). This product is not stable in solution, please use freshly prepared working solution for optimal results. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.54 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (5.54 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.54 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: Saline: 30 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2149 mL | 11.0744 mL | 22.1489 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4430 mL | 2.2149 mL | 4.4298 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2215 mL | 1.1074 mL | 2.2149 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04177498 | Recruiting | Drug: Rigosertib Sodium Other: Quality-of-Life Assessment |
Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa |
Thomas Jefferson University | August 24, 2021 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT04263090 | Completed | Drug: Rigosertib Drug: Nivolumab |
Stage IV Adenocarcinoma |
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai |
June 29, 2020 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT03786237 | Recruiting | Drug: Rigosertib Oral Capsules / Rigosertib Intravenous |
Epidermolysis Bullosa Dystrophica Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Prof. Johann Bauer | April 12, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT05764395 | Recruiting | Drug: Rigosertib Procedure: Biopsy |
Metastatic Melanoma Refractory Melanoma |
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center | May 9, 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02030639 | Completed | Drug: rigosertib | Healthy | Onconova Therapeutics, Inc. | January 2014 | Phase 1 |
28(ON 01910.Na) selectively induces mitotic G2/M arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells.J Med Chem.2011 Sep 22;54(18):6254-76. |
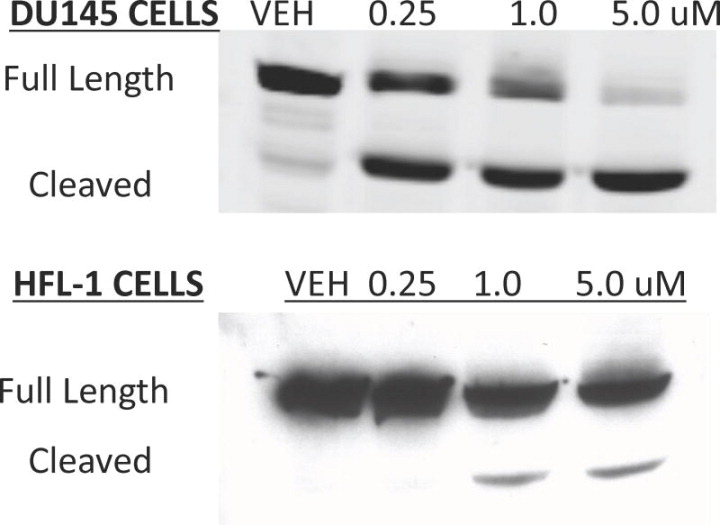 DU145 and HFL-1 (normal human fibroblasts) cells were treated with increasing concentrations of28or DMSO (Vehicle) for 48 h.J Med Chem.2011 Sep 22;54(18):6254-76. DU145 and HFL-1 (normal human fibroblasts) cells were treated with increasing concentrations of28or DMSO (Vehicle) for 48 h.J Med Chem.2011 Sep 22;54(18):6254-76. |
Cellular viability together with the activity of caspases 3/7 were assayed concomitantly in A549 cells treated with28for 24 h (n=3).J Med Chem.2011 Sep 22;54(18):6254-76. |