
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
RITA (also known as NSC-652287) RITA (also known as NSC-652287) is a brand-new and powerful protein-protein interaction inhibitor with potential anticancer activity for the p53-HDM-2 protein. It induces DNA-DNA cross-links and binds to p53dN with a Kd of 1.5 nM.
| Targets |
p53dN (Kd = 1.5 nM)
|
|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
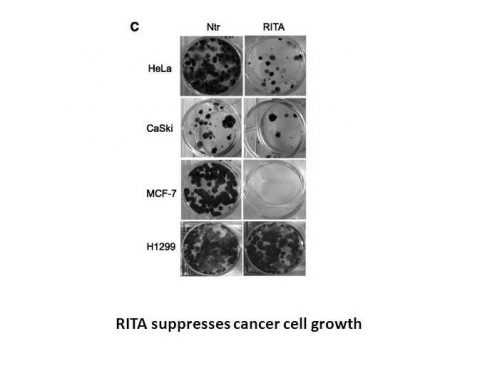
In tumor cell lines, RITA displays a highly selective pattern of differential cytotoxic activity as a result of cellular accumulation to the cytosolic (S100) fraction. With IC50 values of 13 M and 37 M, respectively, RITA also inhibits the growth of other renal cell lines, such as ACHN and UO-31.[1] RITA (10 nM) causes cell cycle arrest with an accumulation of cells in the G2-M phase, and at 100 nM, it causes DNA fragmentation and apoptosis with assessed p53 protein levels in both cases. In A498 cells, RITA (30 nM) also causes DNA-protein and DNA-DNA cross-links. RITA has no impact on the top1-mediated relaxation of supercoiled SV40 DNA in the interim.[2] RITA significantly (97%) inhibits the growth of HCT116 cells, but only marginally (13%), inhibits the growth of HCT116 cells that lack the TP53 gene. In comparison to cell lines lacking p53 and those expressing mutant p53, tumor cell lines expressing wild-type p53 are much more effective at growth inhibition when treated with RITA. The rescue of MDM2's embryonic lethality provides strong evidence that RITA binds full-length p53 but not GST protein or HDM-2 (a key regulator of p53). RITA prevents p53 ubiquitination and interaction with HDM-2. Despite the fact that both proteins are upregulated, RITA significantly reduces the amount of HDM-2 that co-precipitates with p53. RITA blocks interactions between 6XHis-tagged His-HDM-2 proteins and purified GST-p53. [3] RITA has been demonstrated to promote p53Ser46 phosphorylation, which causes apoptosis.[4] RITA induces activation of p53 in conjunction with up-regulation of phosphorylated ASK-1, MKK-4 and c-Jun. RITA induces the activation of JNK signaling.[5] But On the contrary, another results by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) show that RITA does not block the formation of the complex between p53 (residues 1-312) and the N-terminal p53-binding domain of MDM2 (residues 1-118), which is highly probable that the binding of RITA requires native conformation of p53.[6]
|
| ln Vivo |
RITA is well tolerated in mice after intraperitoneal administration, and weight loss is not noticeable at doses up to 10 mg/kg over the course of a month. The growth of the HCT116 tumors is 40% suppressed after five injections of 0.1 mg/kg RITA, with no discernible effects on the HCT116 TP53-/- tumors. RITA exhibits significant antitumor activity at doses of 1 or 10 mg/kg. The growth rate of p53-positive xenografts is reduced by more than a factor of two after five 1 mg/kg injections of RITA, while p53-null xenografts are unaffected. Compared to untreated control mice, mice given 10 mg/kg of RITA had 90% fewer HCT116 tumors. RITA slows the growth of the tumor in a way that is dependent on wild-type p53. [3]
|
| Cell Assay |
The XTT assay is used to evaluate the sensitivity of cells to RITA (0.1 nM - 1 mM). 1500 cells are seeded into each well of 96-well flat-bottom plates, which are then incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 5% air. The wells receive incremental additions of RITA dissolved in DMSO, and 48 hours later, sensitivity is assessed.
|
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: Female SCID mice, 4-6 weeks old, are implanted with subcutaneous xenografts using 1 × 106 cells in 90% Matrigel. After 3-6 days have passed since the cells were injected, palpable tumors have developed, at which point RITA treatment is started. RITA is injected intravenously or intraperitoneally once daily in doses of 0.1, 1 or 10 mg/kg in phosphate buffered saline totaling 100 L. Xenografts are assessed every two days. The average tumor volume for each data point is divided by the average starting tumor volume to plot the tumor volumes for the control and treated groups[1].
|
| References |
| Molecular Formula |
C14H12O3S2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
292.4
|
|
| Exact Mass |
292.0228
|
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 57.51; H, 4.14; O, 16.42; S, 21.93
|
|
| CAS # |
213261-59-7
|
|
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| Appearance |
Solid powder
|
|
| SMILES |
C1=C(SC(=C1)C2=CC=C(O2)C3=CC=C(S3)CO)CO
|
|
| InChi Key |
KZENBFUSKMWCJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H12O3S2/c15-7-9-1-5-13(18-9)11-3-4-12(17-11)14-6-2-10(8-16)19-14/h1-6,15-16H,7-8H2
|
|
| Chemical Name |
[5-[5-[5-(hydroxymethyl)thiophen-2-yl]furan-2-yl]thiophen-2-yl]methanol
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.55 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.55 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.55 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 4: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 30 mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4200 mL | 17.0999 mL | 34.1997 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6840 mL | 3.4200 mL | 6.8399 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3420 mL | 1.7100 mL | 3.4200 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03052036 | Recruiting | Other: Optimal Medical Therapy Procedure: Coronary Angiography |
NSTEMI - Non-ST Segment Elevation MI |
Newcastle-upon-Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust |
November 2016 | |
| NCT05260203 | Completed | Device: RITA (App) | Amyloidosis Myelodysplasia Multiple Myeloma |
Advice Pharma Group srl | June 4, 2022 |
|
|---|
 |