
| Size | Price | Stock | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
Purity: ≥98%
Tamatinib besylate (formerly R-406 besylate; prodrug of R 406) is a novel, potent and ATP-competitive inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase/Syk with potential anti-inflammatory activity. In cell-free assays, it inhibits Syk with an IC50 of 41 nM. Syk is essential for the signaling that activates B-cell receptors (BCR) and Fc receptors. Tamatinib is five times less effective against Flt3 and significantly inhibits Syk but not Lyn. It may be used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, other autoimmune diseases, and the inflammation linked to bronchial asthma caused by allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR).
| Targets |
Syk (Ki = 30 nM); Syk (IC50 = 41 nM); Lyn (IC50 = 63 nM); Lck (IC50 = 37 nM); FLT3
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
R406 is serially diluted in DMSO, diluted in kinase buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mg/mL acetylated BGG) and finally diluted to 1% DMSO by volume. After adding ATP and substrate to kinase buffer at room temperature, the final DMSO concentration is 0.2%. 0.125 ng of Syk is added to kinase buffer to initiate the kinase reactions, which are carried out in a final volume of 20 mL with 5 mM HS1 peptide substrate and 4 mM ATP. The reaction is left to continue at room temperature for forty minutes. 20 mL of PTK quench mix containing EDTA, anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (1X final), and fluorescent phosphopeptide tracer (0.5X final) diluted in FP Dilution Buffer is added to stop the reaction. A Polarion fluorescence polarization plate reader is used to read the plate after it has been incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark. Through competition with the phosphopeptide competitor included in the Tyrosine Kinase Assay Kit, a calibration curve is created that is used to convert data into the amount of phosphopeptide present. Non-linear regression analysis is used to fit the curve and test R406 at eleven different concentrations in order to determine the IC5
|
||
| Cell Assay |
R406 is applied in serial dilutions (0.3, 0.6, 1.25, 2.5, or 5 μM) to DLBCL cell lines for either 72 or 96 hours. After that, the MTT assay is used to measure cellular proliferation, and the annexin V–FITC/propidium iodide (PI) staining is used to evaluate cell apoptosis. Cells are lysed, size-fractionated using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), and immunoblotted to determine the presence of caspase 9, 8, and 3.
Researchers investigated the effect of R406, a small molecule inhibitor of Syk developed as a potential treatment of autoimmune diseases, allergic disorders and B-cell related hematological malignancies, on FcγRIIA-mediated platelet activation. To further assess the potential activity of Syk inhibitors in HIT treatment, the effect of R406 was also evaluated on HIT antibodies-induced expression of TF and procoagulant activity of monocytic cells. Results: We show that R406 is a potent inhibitor of platelet signaling and functions initiated by FcγRIIA cross-linking by specific antibodies or by sera from HIT patients. Syk inhibition efficiently prevents FcγRIIA-induced LAT phosphorylation and activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, Akt, phospholipase Cγ2 and p38 MAP-kinase. As a consequence, FcγRIIA-induced platelet aggregation, granule secretion and microparticles production are strongly inhibited by R406. Moreover, the Syk inhibitor efficiently impairs the expression of TF and the procoagulant activity of human monocytes triggered by HIT antibodies. Conclusion: Syk inhibitors may be of therapeutic interest in the treatment of HIT by reducing HIT antibodies-mediated platelet activation and monocyte procoagulant activity [3]. |
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References | |||
| Additional Infomation |
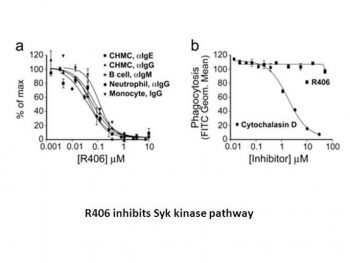
Recent compelling evidence has lead to renewed interest in the role of antibodies and immune complexes in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis. These immune complexes, consisting of autoantibodies to self-antigens, can mediate inflammatory responses largely through binding and activating the immunoglobulin Fc receptors (FcRs). Using cell-based structure activity relationships with cultured human mast cells, we have identified the small molecule R406 [N4-(2,2-dimethyl-3-oxo-4H-pyrid[1,4]oxazin-6-yl)-5-fluoro-N2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2,4-pyrimidinediamine] as a potent inhibitor of immunoglobulin E (IgE)- and IgG-mediated activation of Fc receptor signaling (EC(50) for degranulation = 56-64 nM). Here we show that the primary target for R406 is the spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), which plays a key role in the signaling of activating Fc receptors and the B-cell receptor (BCR). R406 inhibited phosphorylation of Syk substrate linker for activation of T cells in mast cells and B-cell linker protein/SLP65 in B cells. R406 bound to the ATP binding pocket of Syk and inhibited its kinase activity as an ATP-competitive inhibitor (K(i) = 30 nM). Furthermore, R406 blocked Syk-dependent FcR-mediated activation of monocytes/macrophages and neutrophils and BCR-mediated activation of B lymphocytes. R406 was selective as assessed using a large panel of Syk-independent cell-based assays representing both specific and general signaling pathways. Consistent with Syk inhibition, oral administration of R406 to mice reduced immune complex-mediated inflammation in a reverse-passive Arthus reaction and two antibody-induced arthritis models. Finally, we report a first-inhuman study showing that R406 is orally bioavailable, achieving exposures capable of inhibiting Syk-dependent IgE-mediated basophil activation. Collectively, the results show R406 potential for modulating Syk activity in human disease.[1]
Antigenic stimulation through the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) is considered to promote the expansion of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells. The spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), a key component of BCR signaling, can be blocked by R406, a small-molecule Syk inhibitor, that displayed activity in CLL patients in a first clinical trial. In this study, we investigated the effects of BCR stimulation and R406 on CLL cell survival and migration. The prosurvival effects promoted by anti-IgM stimulation and nurselike cells were abrogated by R406. BCR triggering up-regulated adhesion molecules, and increased CLL cell migration toward the chemokines CXCL12 and CXCL13. BCR activation also enhanced CLL cell migration beneath marrow stromal cells. These responses were blocked by R406, which furthermore abrogated BCR-dependent secretion of T-cell chemokines (CCL3 and CCL4) by CLL cells. Finally, R406 inhibited constitutive and BCR-induced activation of Syk, extracellular signal-regulated kinases, and AKT, and blocked BCR-induced calcium mobilization. These findings suggest that BCR activation favors CLL cell homing, retention, and survival in tissue microenvironments. R406 effectively blocks these BCR-dependent responses in CLL cells, providing an explanation for the activity of R406 in patients with CLL.[2] Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) is a novel pharmaceutical target for treatment of allergic, autoimmune, and neoplastic disorders. Previous studies have indicated that Syk signaling plays critical roles in regulating the lymphohematopoietic system. These observations prompted us to investigate whether inhibition of Syk would promote immunotoxicity. In a series of studies, rats were treated orally with R406, at dose levels up to and including 100 mg/kg/day (or its prodrug R788 at dose levels up to and including 100 mg/kg/day, reduced to 50 mg/kg/day for females as MTD was exceeded), a potent Syk inhibitor, twice daily for 28 days. In addition to standard toxicological assessments, immunophenotyping by flow cytometric analysis, and a study of humoral immune response measuring anti-KLH IgM and IgG levels, were undertaken. Other immunotoxicity studies included three host resistance models in female Balb/c mice to further ascertain effects of R406 on innate and acquired immunity. Following R406 treatment, expected immunomodulating effects (e.g., decreased thymic and spleen weight, hypocellularity of bone marrow, and reduced lymphocyte counts, including T and B cells) were observed in the rat studies. These changes essentially resolved during a 14-day treatment-free recovery period. A KLH challenge in rats demonstrated no adverse effects on IgG or IgM response. R788/406, administered orally at dose levels up to and including 80 mg/kg/day for 28 days, did not affect bacterial or viral clearance in the Listeria, Streptococcal, or Influenza host resistance mouse models, respectively. This correlated with previous in vitro macrophage and neutrophil function assays (assessing migration, phagocytosis, oxidative burst and microbicidal activity), which revealed that R406 did not adversely affect macrophage or neutrophil function in innate immune responses. Collectively, these results demonstrate that R406 has minimal functional immunotoxicity notwithstanding its lymphocytopenic effect, suggesting that inhibition of Syk might not lead to unacceptable mechanism-based adverse effects. [3] |
| Molecular Formula |
C28H29FN6O8S
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
628.63
|
| Exact Mass |
628.175
|
| Elemental Analysis |
C, 53.50; H, 4.65; F, 3.02; N, 13.37; O, 20.36; S, 5.10
|
| CAS # |
841290-81-1
|
| Related CAS # |
R406 free base;841290-80-0
|
| PubChem CID |
11984591
|
| Appearance |
Light yellow to khaki solid powder
|
| LogP |
5.227
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
4
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
14
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
8
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
44
|
| Complexity |
874
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C1C(C)(C)OC2C(=NC(NC3C(F)=CN=C(NC4C=C(OC)C(OC)=C(OC)C=4)N=3)=CC=2)N1.O=S(C1C=CC=CC=1)(O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
UXDRJPYSTZHIOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H23FN6O5.C6H6O3S/c1-22(2)20(30)28-19-13(34-22)6-7-16(27-19)26-18-12(23)10-24-21(29-18)25-11-8-14(31-3)17(33-5)15(9-11)32-4;7-10(8,9)6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h6-10H,1-5H3,(H3,24,25,26,27,28,29,30);1-5H,(H,7,8,9)
|
| Chemical Name |
benzenesulfonic acid;6-[[5-fluoro-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyanilino)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2,2-dimethyl-4H-pyrido[3,2-b][1,4]oxazin-3-one
|
| Synonyms |
R406 benzenesulfonate; R-406 benzenesulfonate; R-406 besylate; R406; R-406; R 406; R 406 besylate; R406 Benzenesulfonate; Tamatinib besylate; R406 besylate; 6-((5-fluoro-2-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2,2-dimethyl-2H-pyrido[3,2-b][1,4]oxazin-3(4H)-one benzenesulfonate; 6-[[5-fluoro-2-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)amino]-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2,2-dimethyl-2H-pyrido[3,2-b]-1,4-oxazin-3(4H)-one benzenesulfonate; 841290-81-1 (besylate); R406 besylate; R406 benzenesulfonate; Tamatinib
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.
For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (3.98 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. View More
Solubility in Formulation 3: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol: 30mg/mL |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5908 mL | 7.9538 mL | 15.9076 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3182 mL | 1.5908 mL | 3.1815 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1591 mL | 0.7954 mL | 1.5908 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Calculation results
Working concentration: mg/mL;
Method for preparing DMSO stock solution: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO (stock solution concentration mg/mL). Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation::Take μL DMSO stock solution, next add μL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O,mix and clarify.
(1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
(2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00798096 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Fostamatinib Disodium | T Cell Lymphoma | Rigel Pharmaceuticals | March 2009 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00923481 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Fostamatinib disodium | Head and Neck Neoplasms Pheochromocytoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) | April 2009 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02077192 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Fostamatinib Disodium | Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura | Rigel Pharmaceuticals | October 2014 | Phase 3 |
| NCT00706342 | Completed Has Results | Drug: Fostamatinib Disodium / R935788 | Purpura, Thrombocytopenic, Idiopathic | Rigel Pharmaceuticals | January 2007 | Phase 2 |
|
 |
The Syk inhibitor R406 induces CLL cell apoptosis and abrogates BCR-derived survival signals. Blood. 2009 Jul 30; 114(5): 1029–1037. |